Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
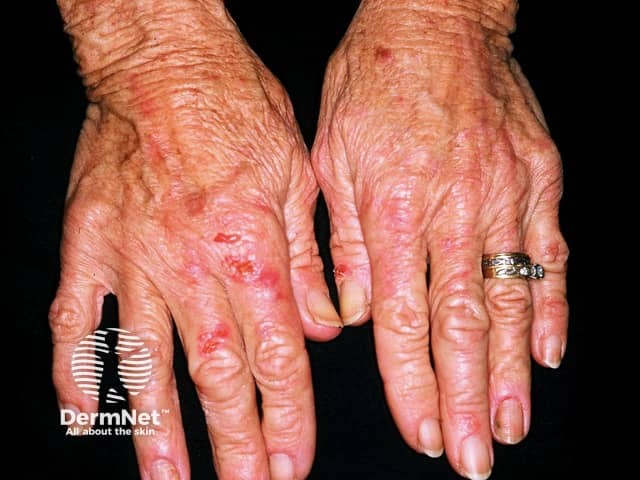
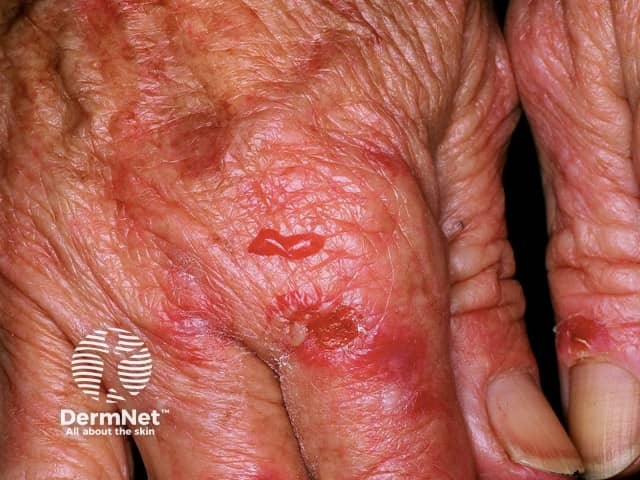
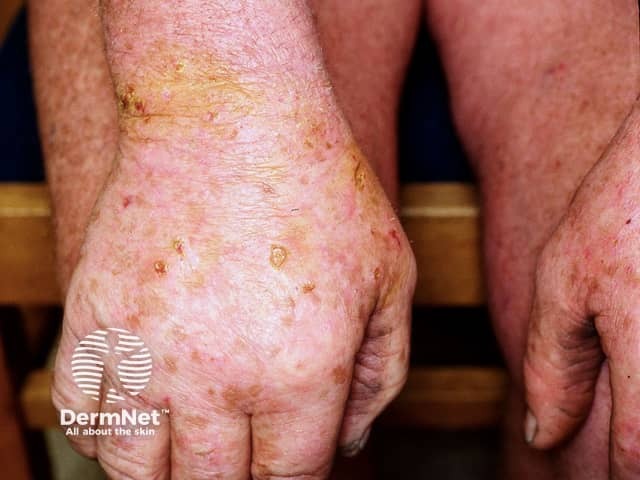
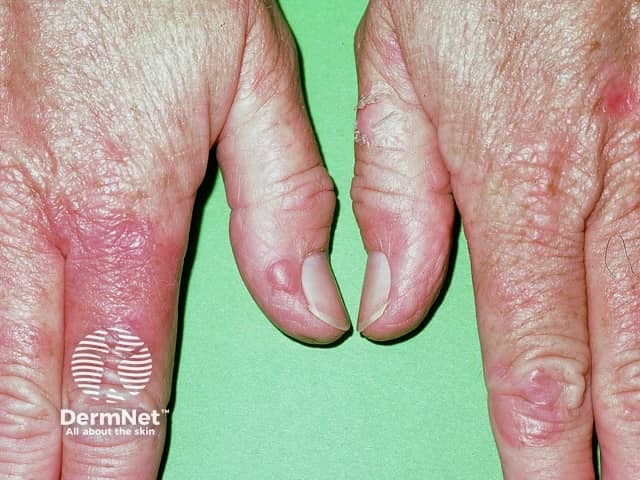
Pseudoporphyria is a condition which closely resembles true cutaneous porphyria (porphyria cutanea tarda, variegate porphyria) but porphyrin tests are normal.
Skin signs include skin fragility and photosensitivity. Tense blisters form at the sites of minor trauma on sun exposed skin, bursting early to leave scabs and erosions. The blisters are most often seen on the hands and feet. They sometimes heal with some scar formation and tiny white cysts under the skin (milia).
A sunburn type rash may also occur.
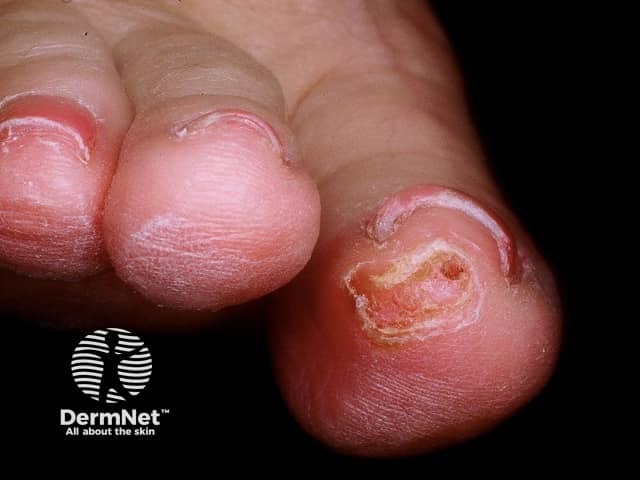
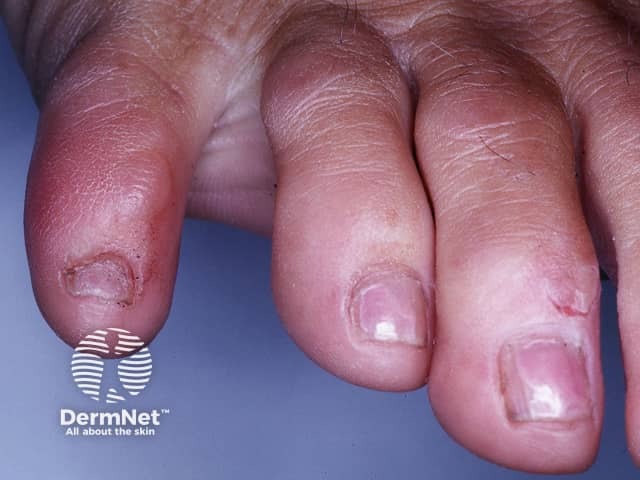
Pseudoporphyria is generally due to drugs or other agents which interact with sunlight to cause a phototoxic reaction in the skin. These include:
It may be provoked by:
If there is clinical doubt, biochemical tests will be done to exclude true cutaneous porphyria. This may include blood, urine and faeces samples.
A skin biopsy may be taken from a blister.
Phototesting can be done to confirm to confirm a phototoxic action of the suspected agent.
It is important to withdraw the suspected agent where possible and avoid unnecessary exposure to strong light.
Sun protection measures may include UVB and UVA blocking sunscreens.
Symptoms usually resolve within several weeks but sometimes they are persistent.