Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, February 2016.
Introduction
Questions to consider
Very itchy skin with localised rash
Mildly itchy skin with localised rash
Very itchy skin with generalised rash
Mildly itchy skin with generalised rash
Localised itchy skin without rash
Generalised itchy skin without rash
Itch is defined by a desire to scratch.
An acute or chronic itchy rash is most often due to dermatitis/eczema. Dermatitis can be primary, or secondary to scratching.
Stages include:
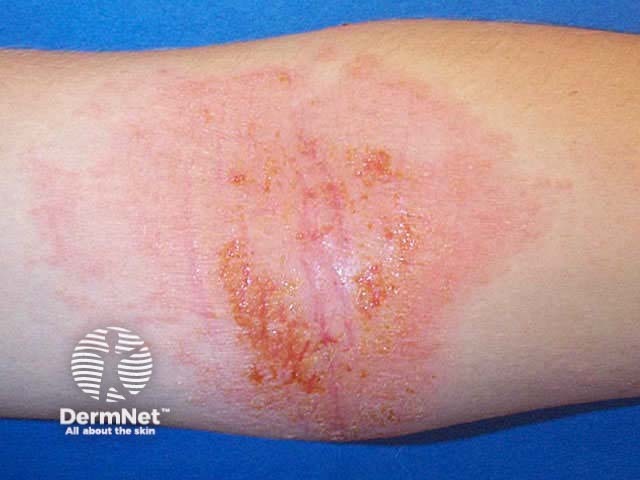
Acute dermatitis
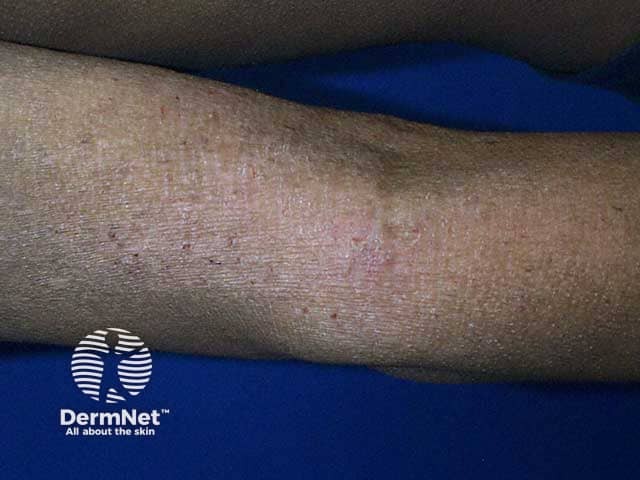
Chronic dermatitis
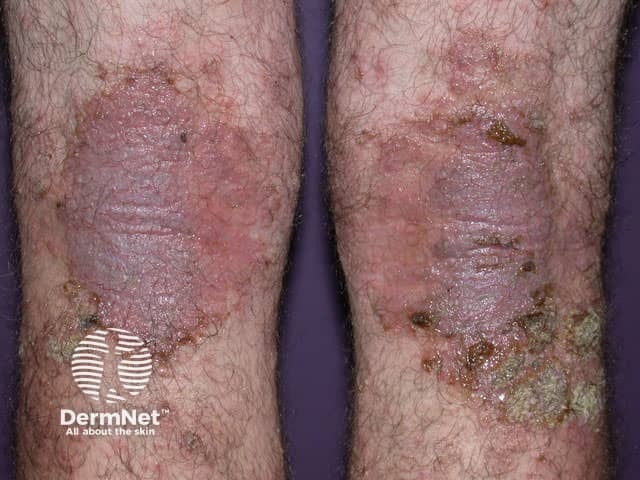
Infected dermatitis
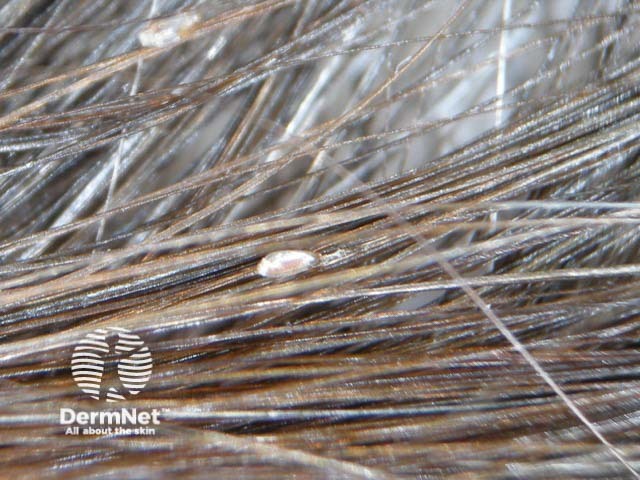

Dermatoscopic examination of hair shaft
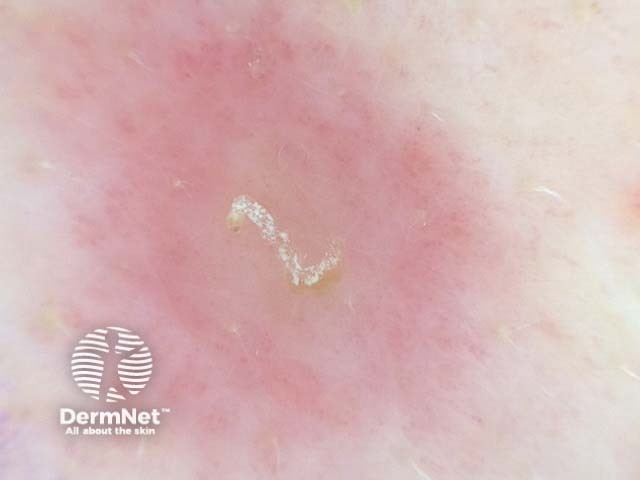
Dermatoscopic examination of possible burrows
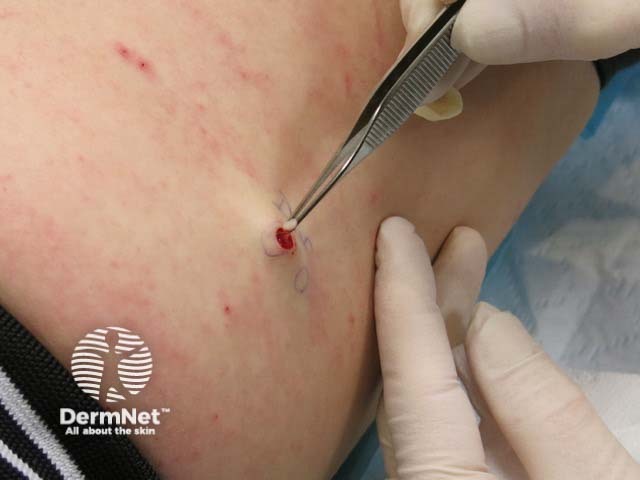
Skin biopsy for histopathology
General treatments for itchy skin conditions may include:
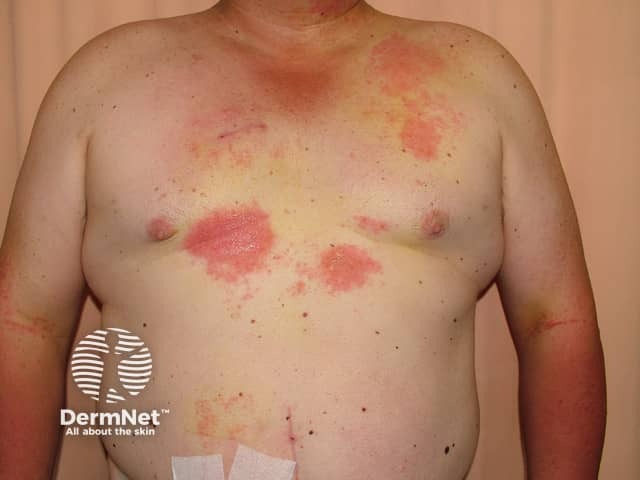
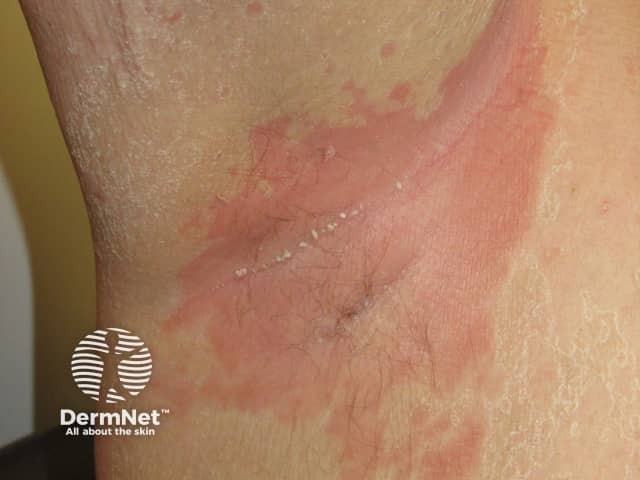
Contact dermatitis
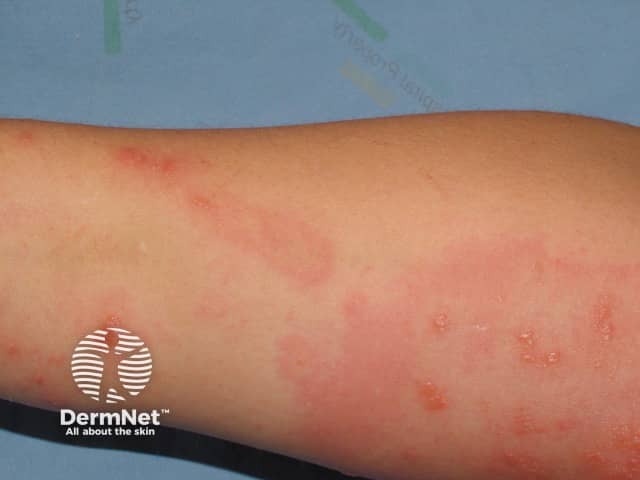
Contact dermatitis
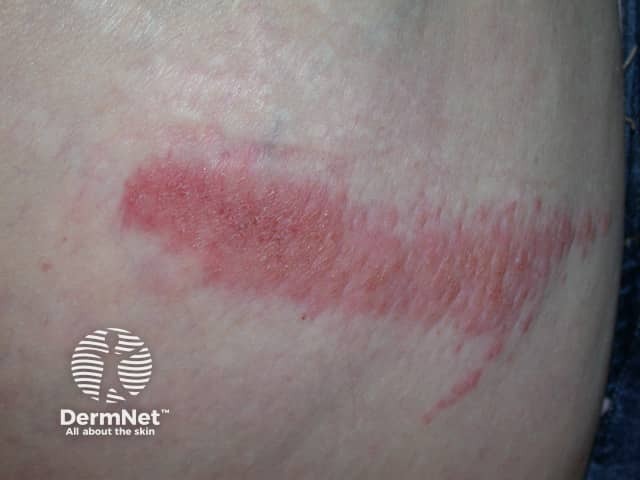
Contact dermatitis
Insect bites / papular urticaria
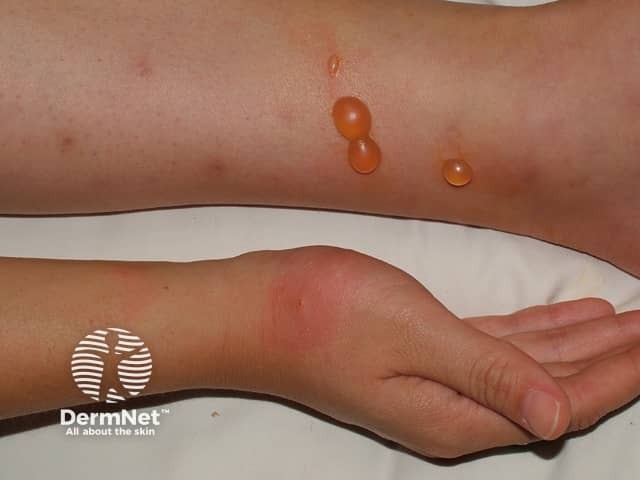
Insect bites
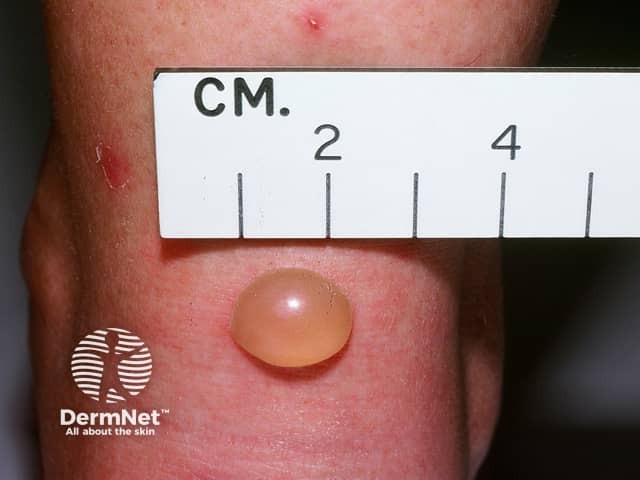
Insect bites
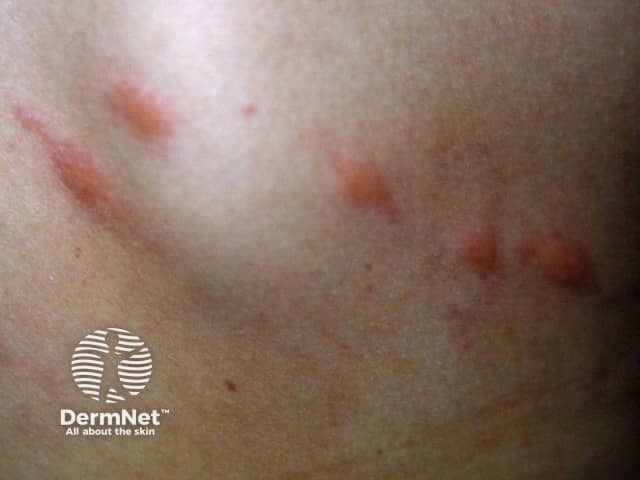
Insect bites
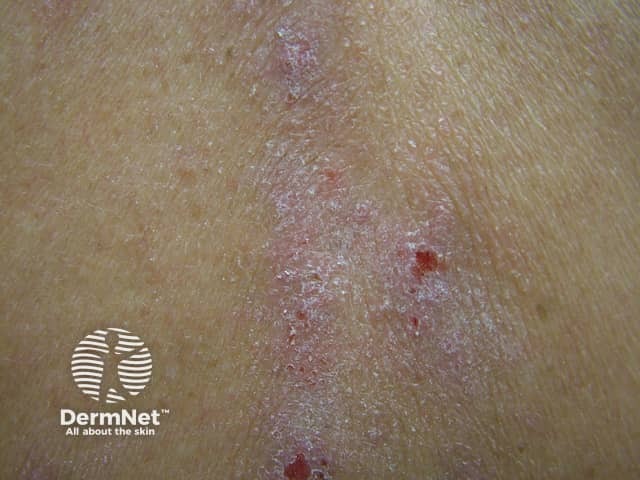
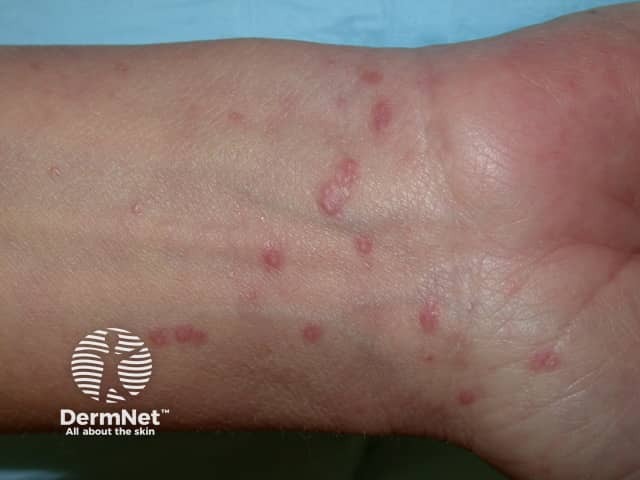
Lichen planus
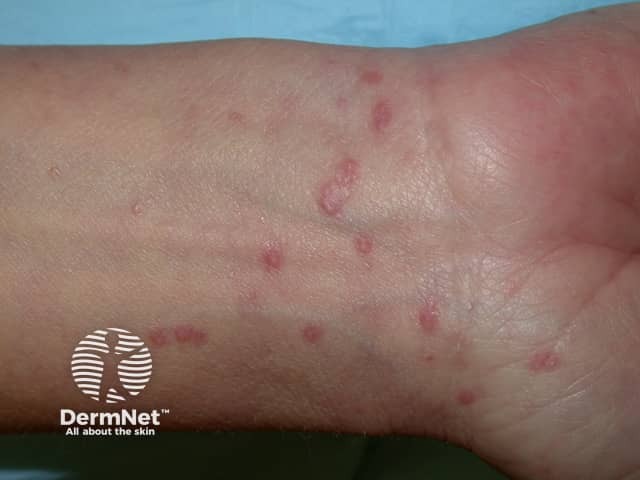
Lichen planus
Lichen planus
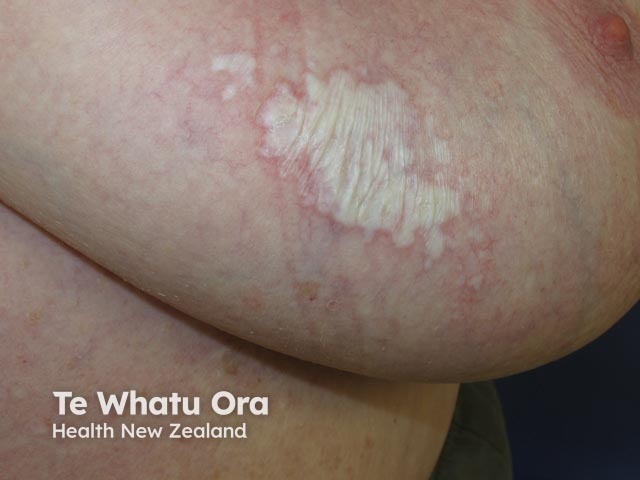
Lichen sclerosus
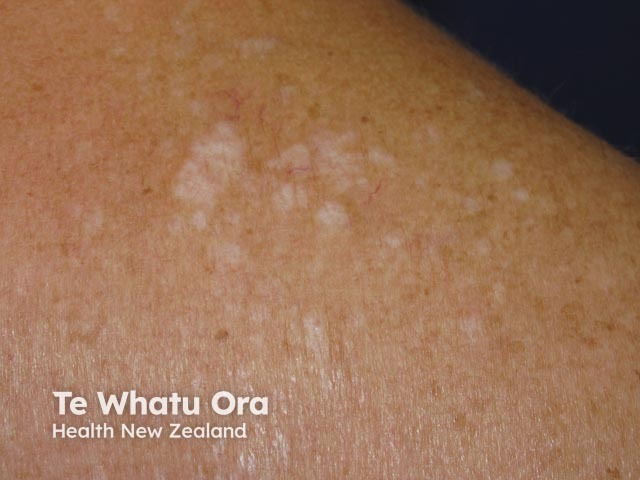
Lichen sclerosus
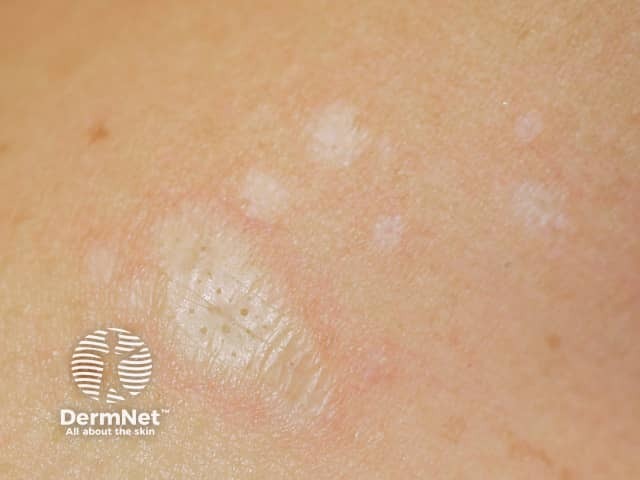
Lichen sclerosus
Lichen simplex
Lichen simplex
Lichen simplex
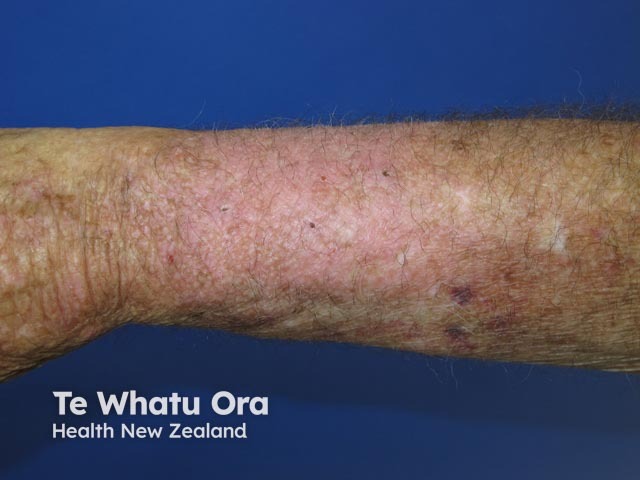
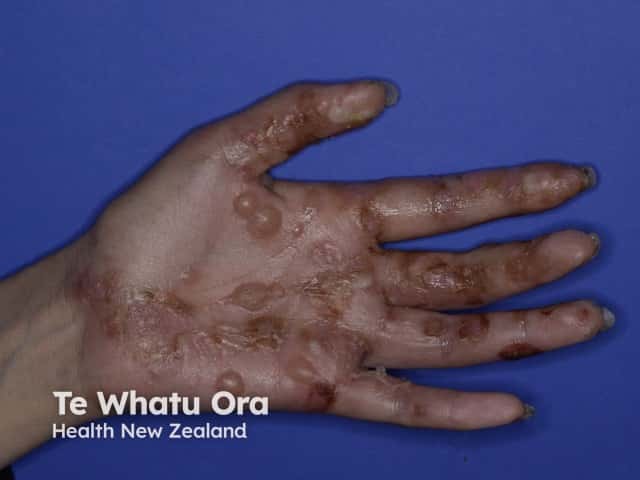
Pompholyx (dyshidrotic eczema)
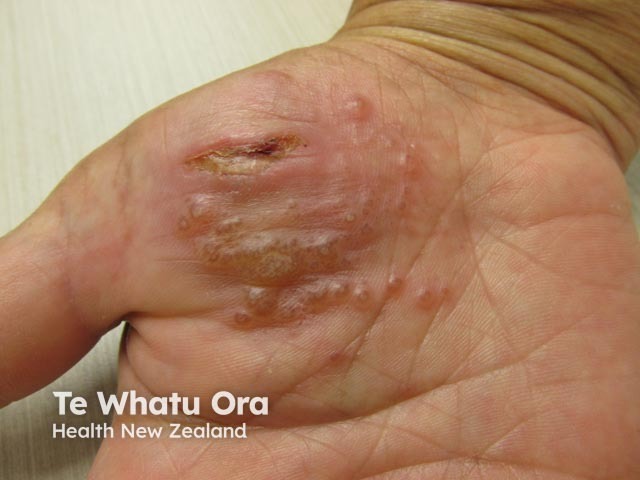
Pompholyx
Pompholyx
Pompholyx
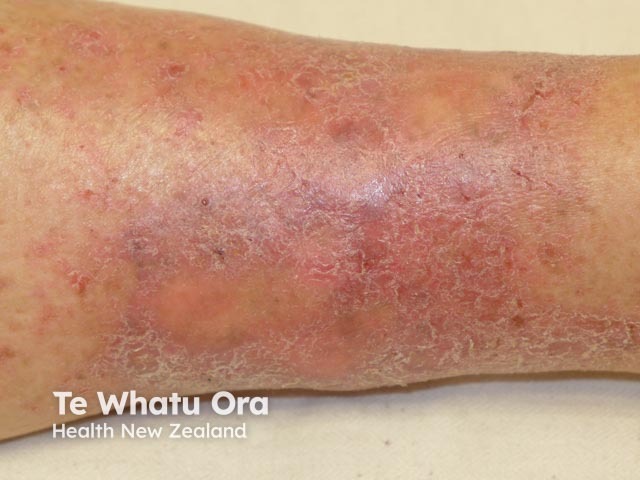
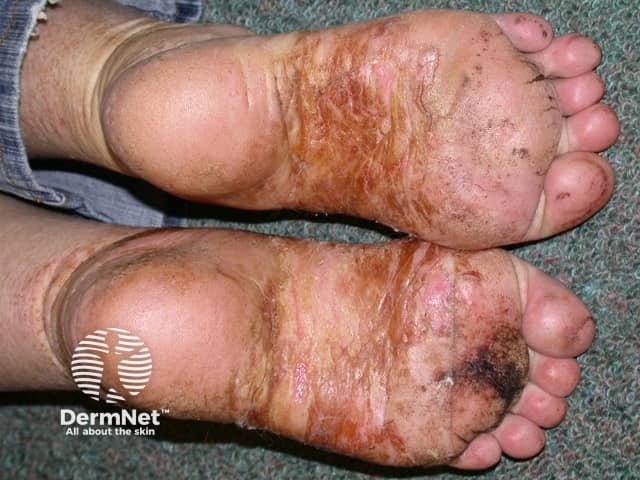
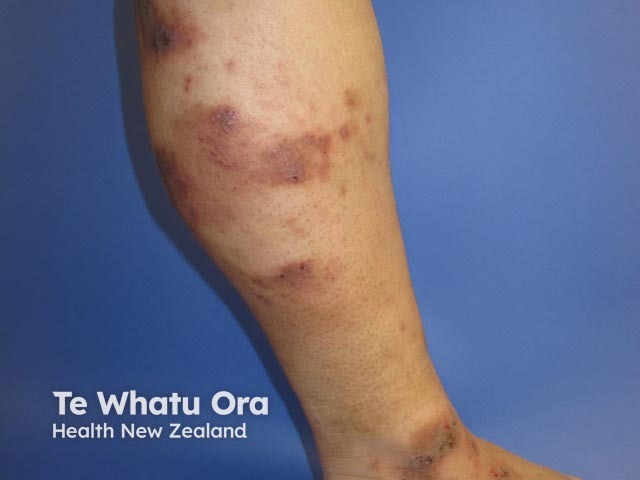
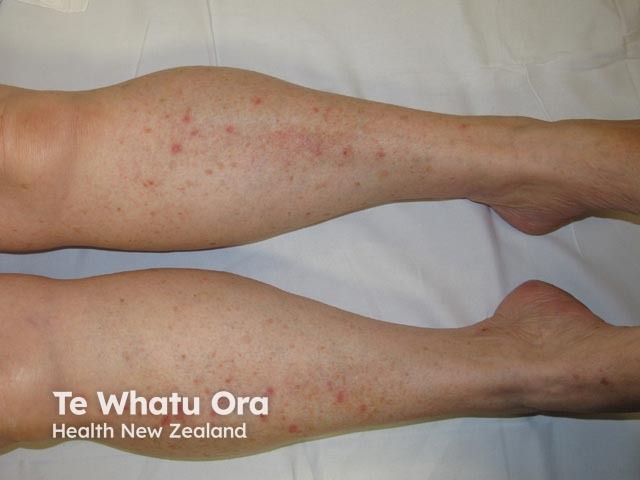
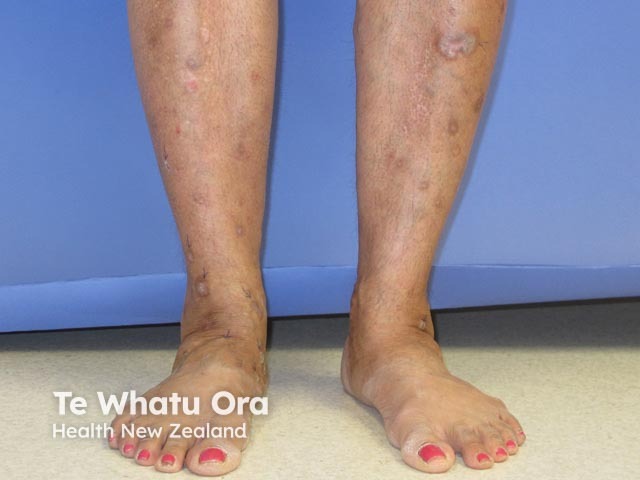
Venous eczema
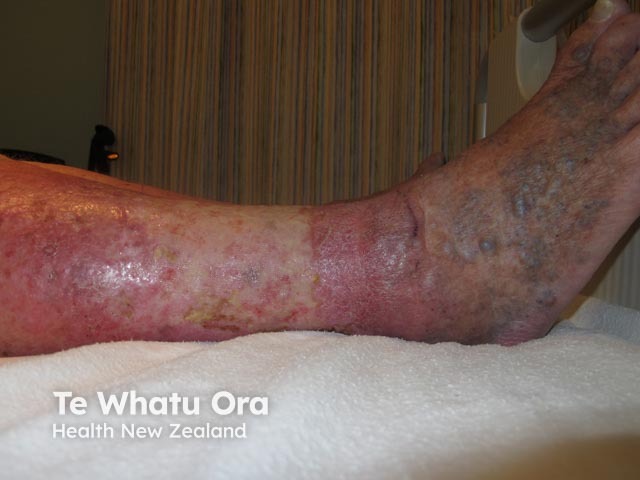
Venous eczema
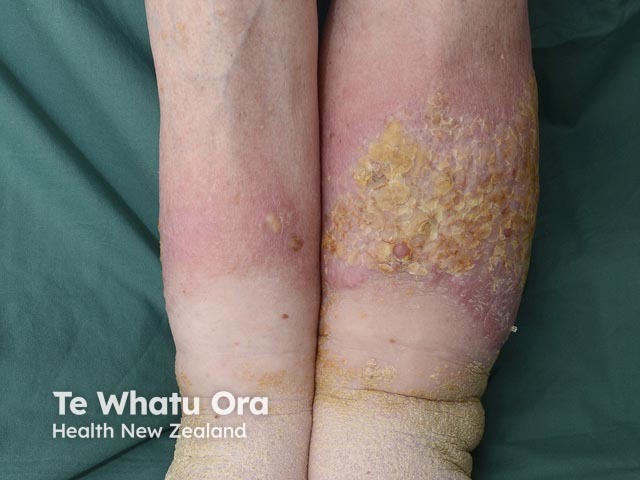
Venous eczema
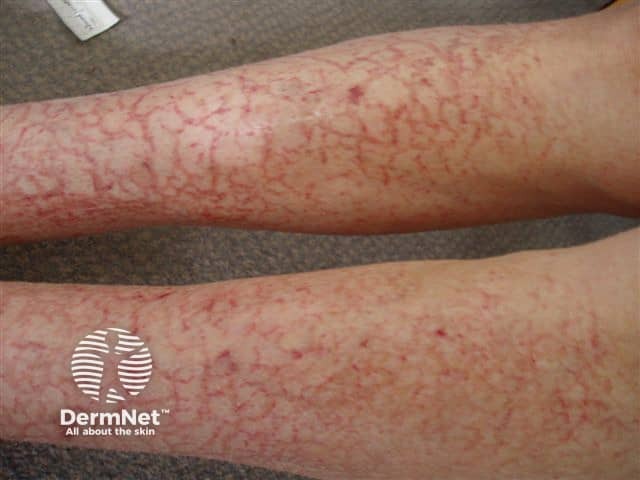
Venous eczema
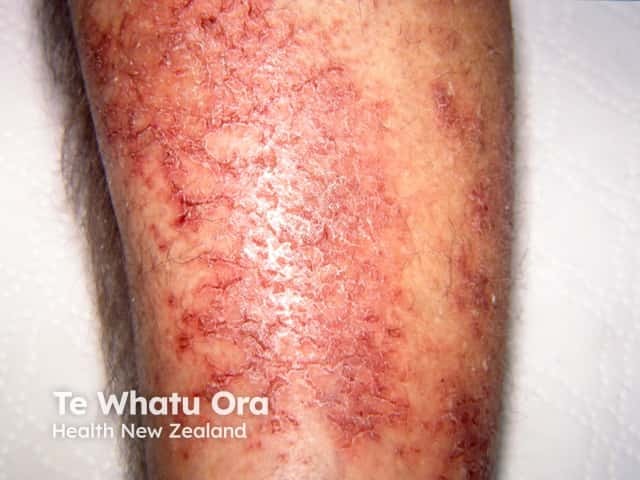
Venous eczema
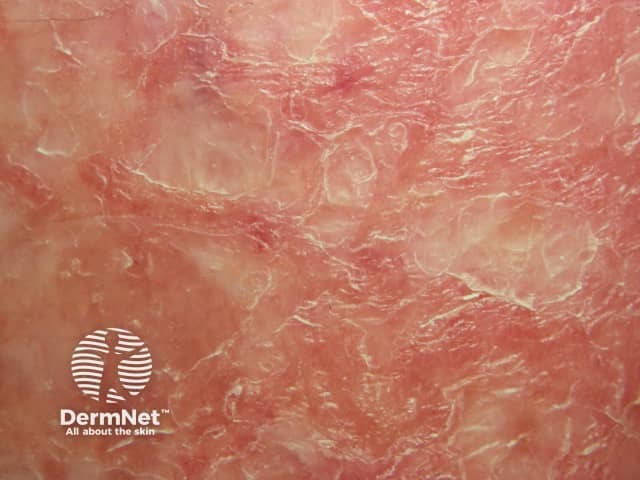
Venous eczema
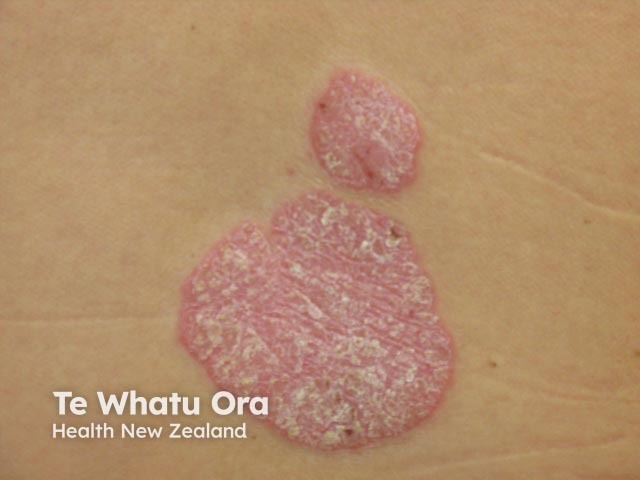
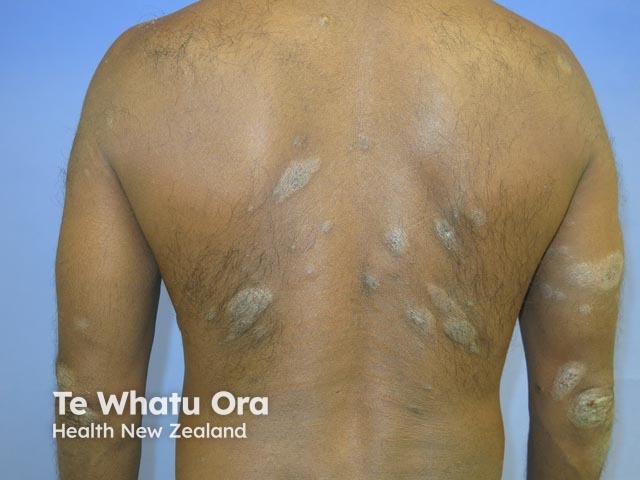
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
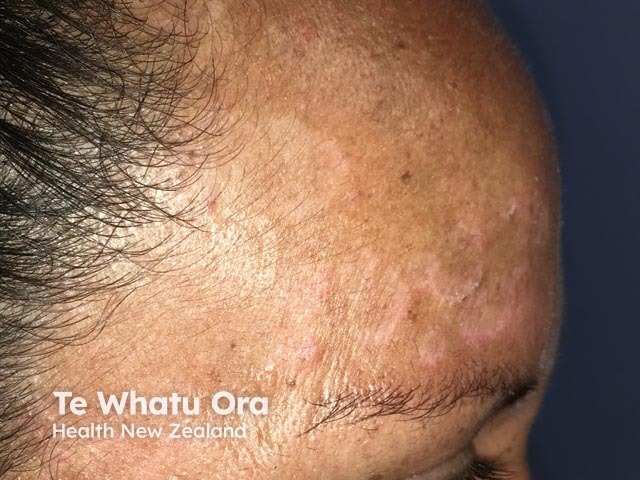
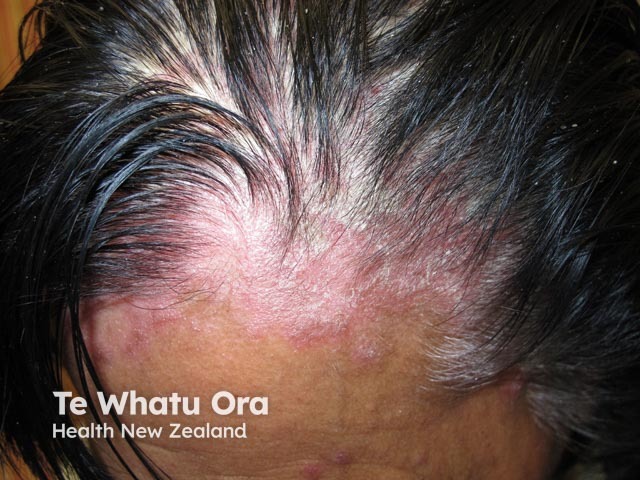
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
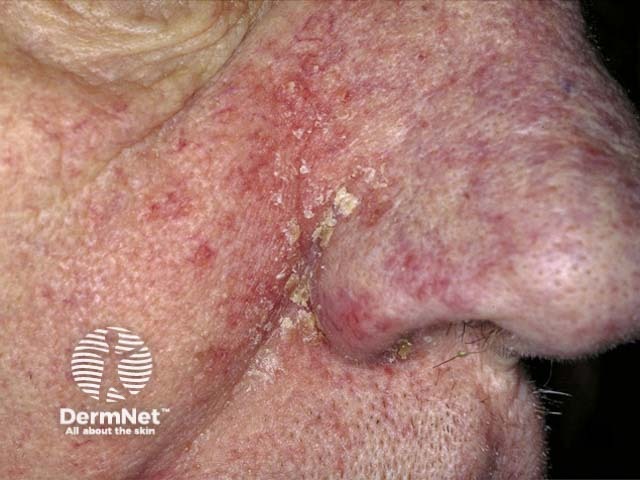
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
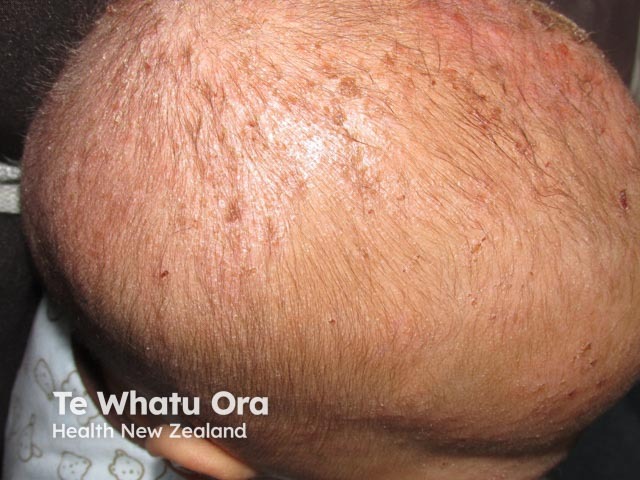
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
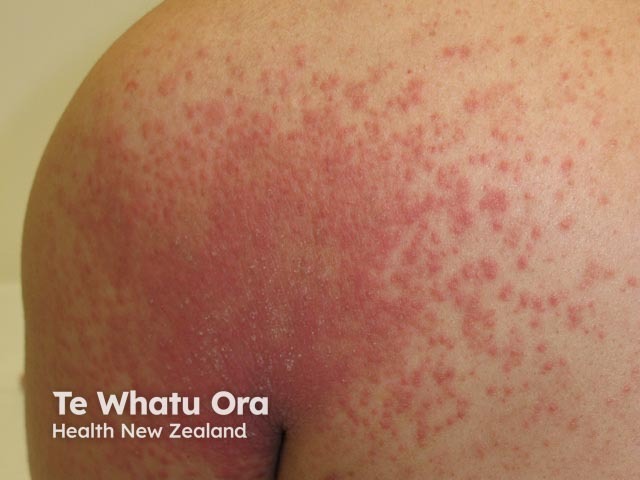
Autoeczematisation
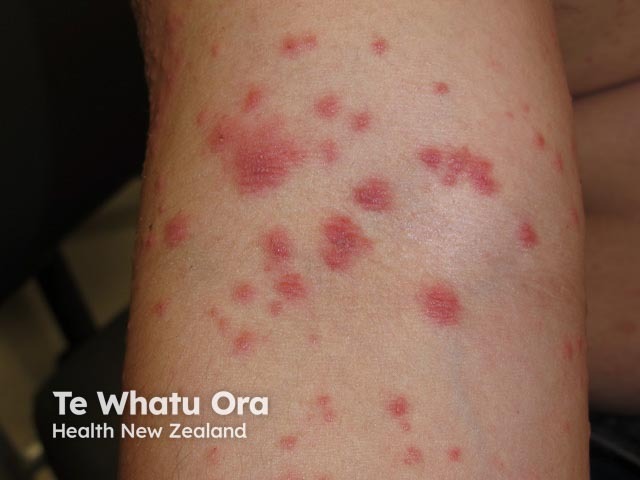
Autoeczematisation
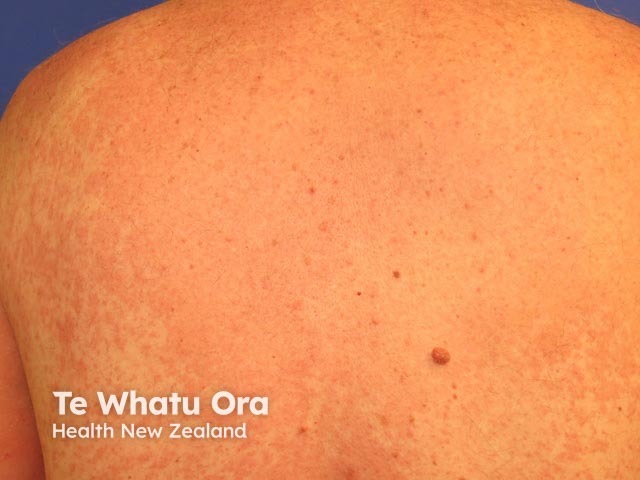

Autoeczematisation
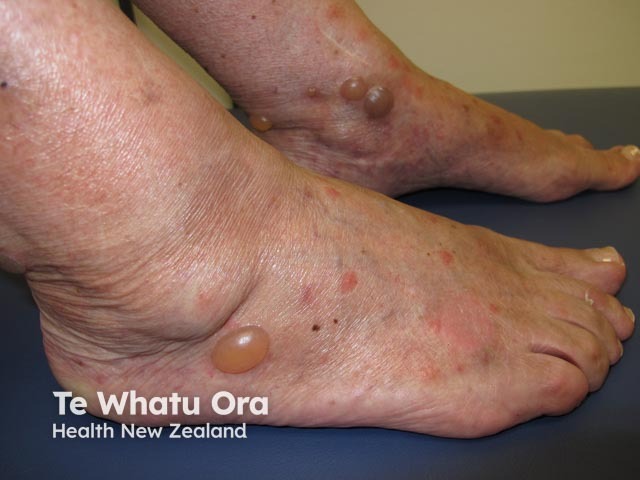
Bullous pemphigoid
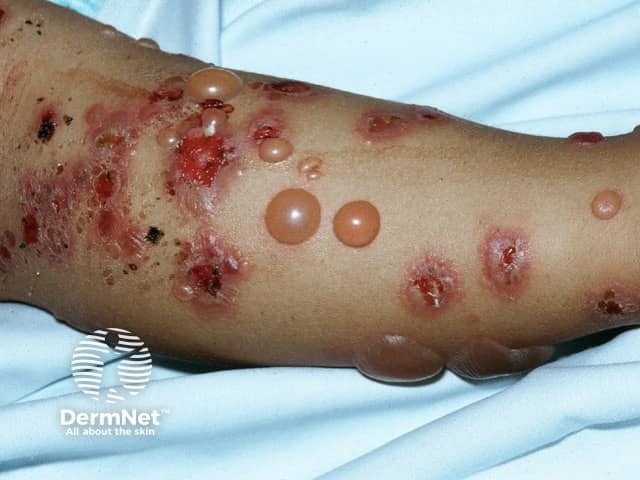
Bullous pemphigoid
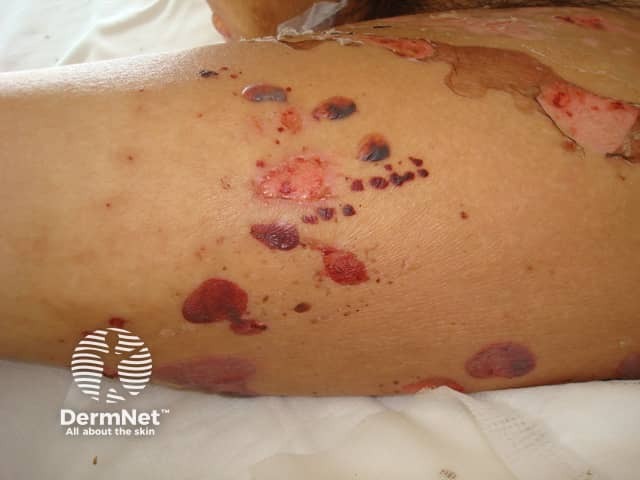
Bullous pemphigoid
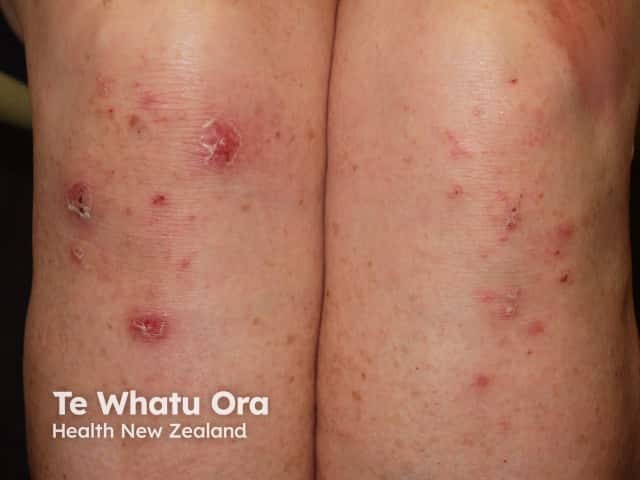
Dermatitis herpetiformis
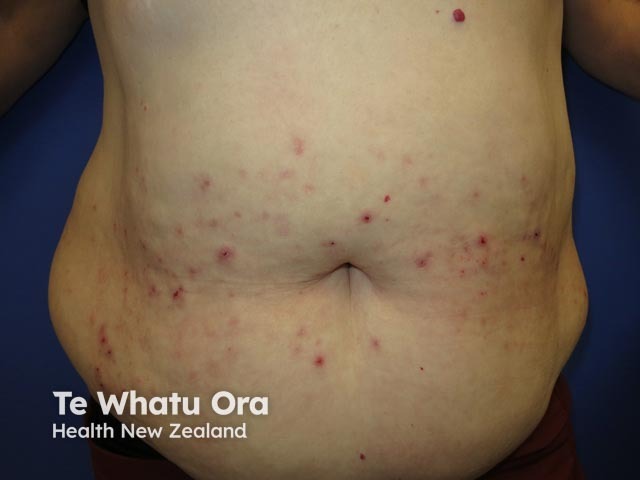
Dermatitis herpetiformis
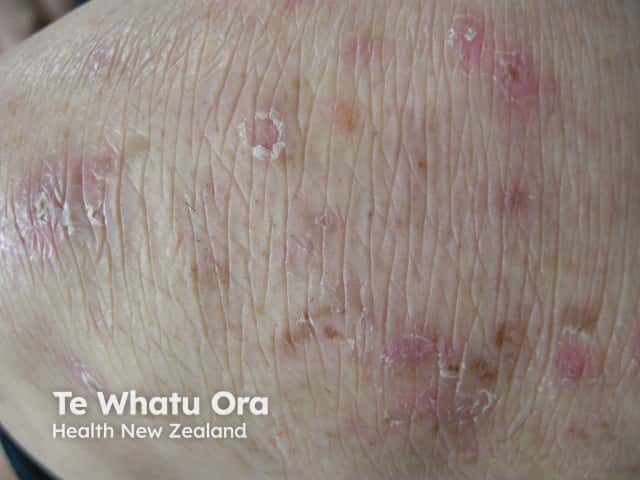
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Atopic dermatitis
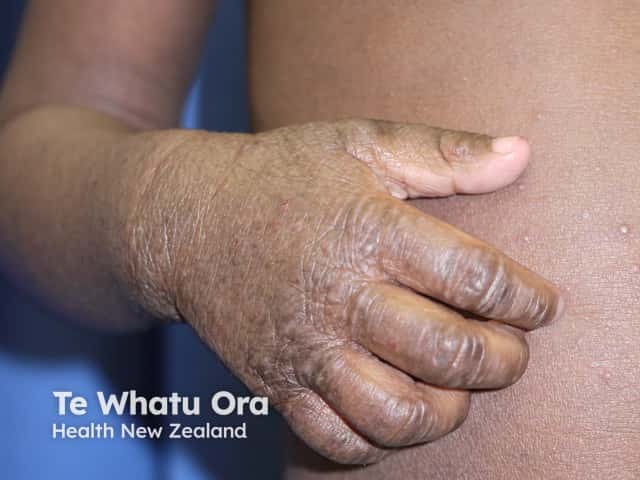
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
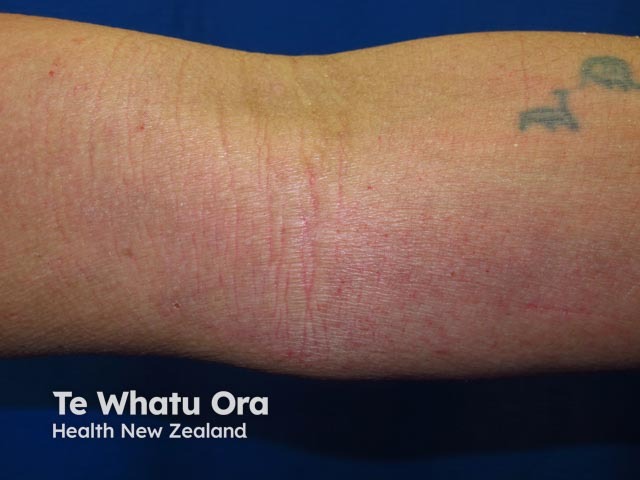
Discoid eczema
Discoid eczema
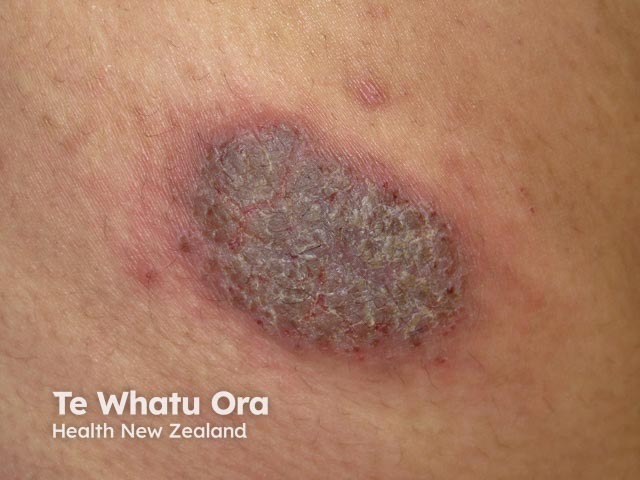
Discoid eczema
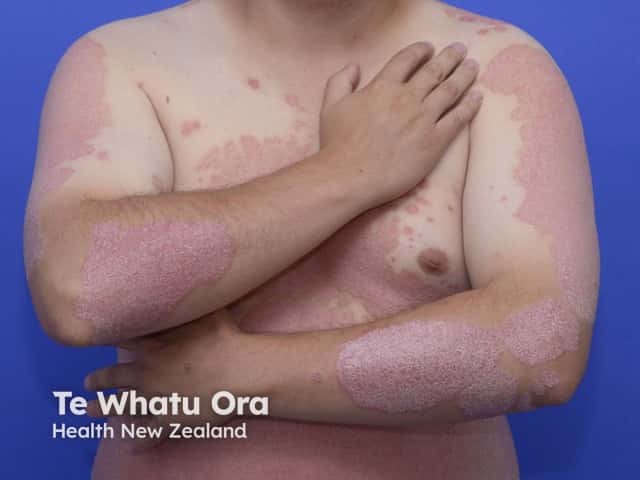
Erythroderma
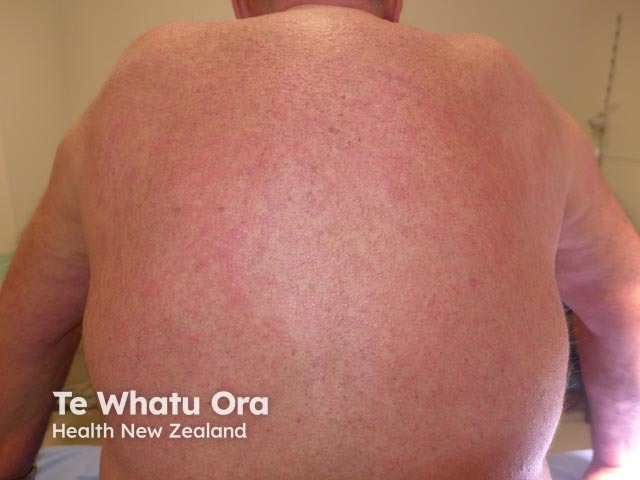
Erythroderma
Erythroderma
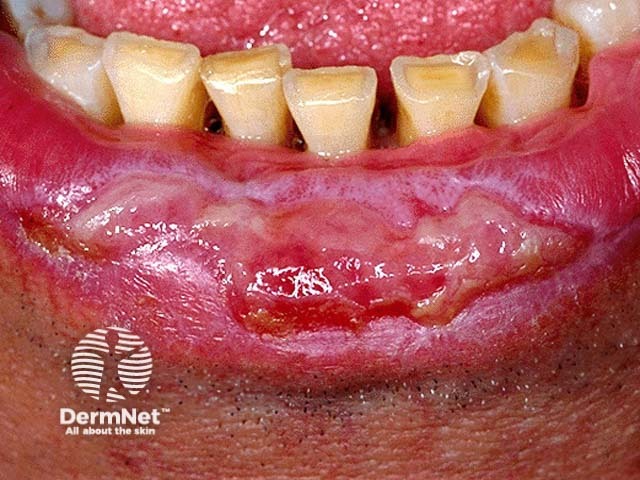
Lichen planus
Lichen planus
Lichen planus
Mycosis fungoides (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma)
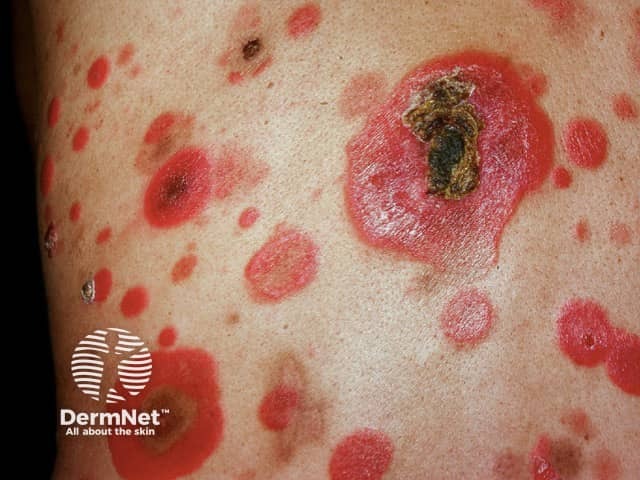
Mycosis fungoides
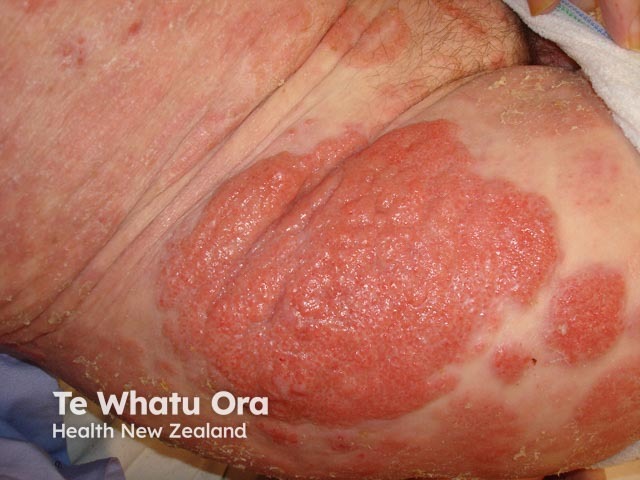
Mycosis fungoides
Mycosis fungoides
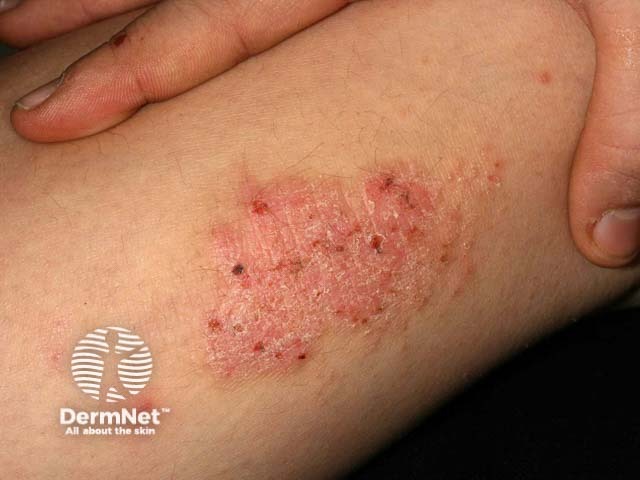
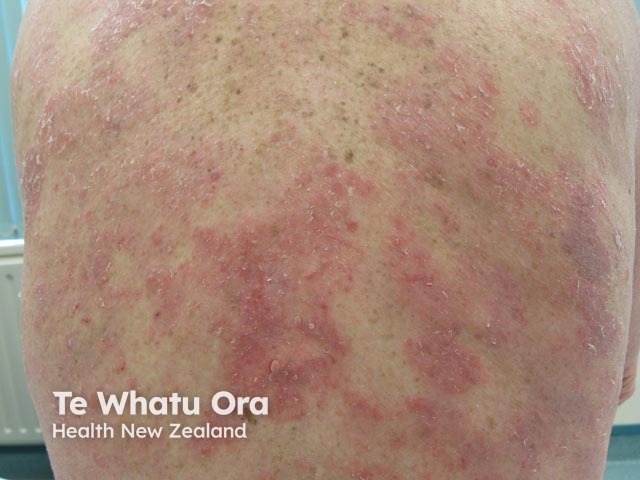
Neurodermatitis
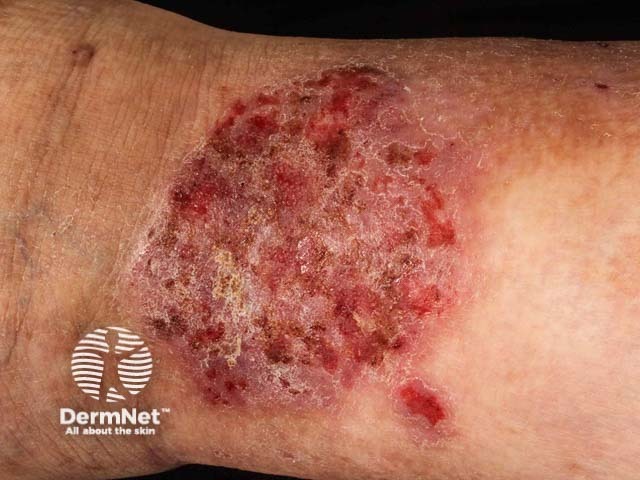
Neurodermatitis
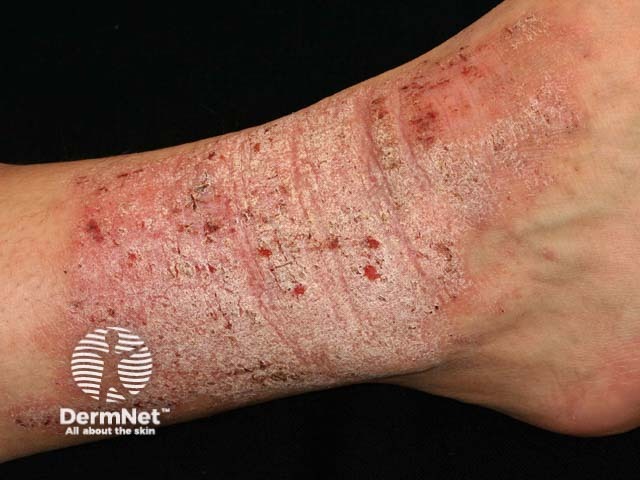
Neurodermatitis
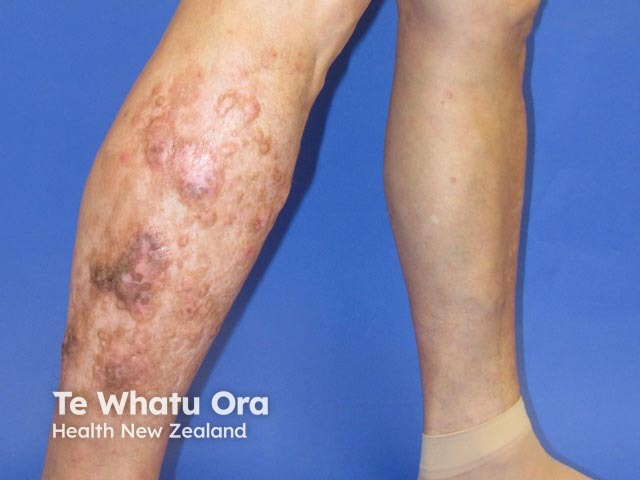
Nodular prurigo
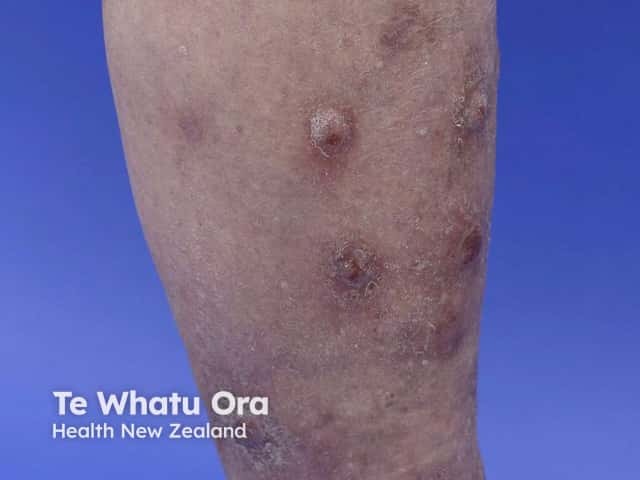
Nodular prurigo
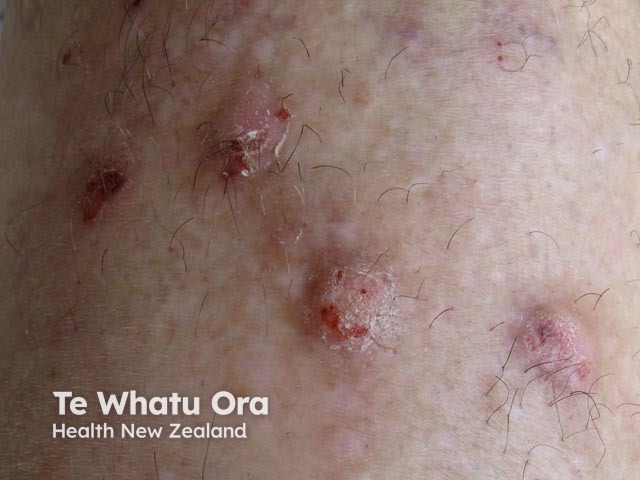
Nodular prurigo
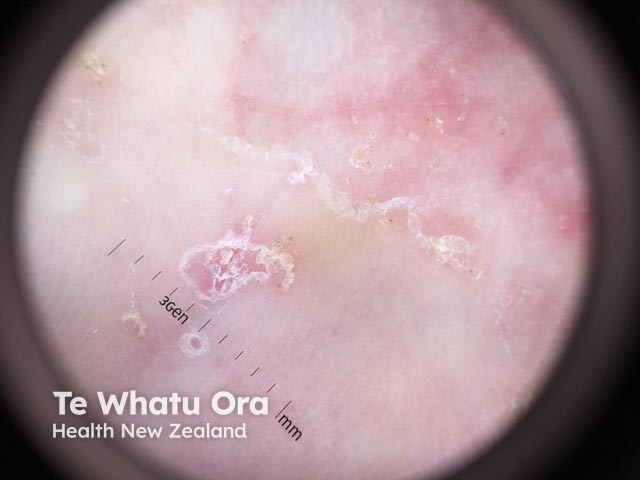
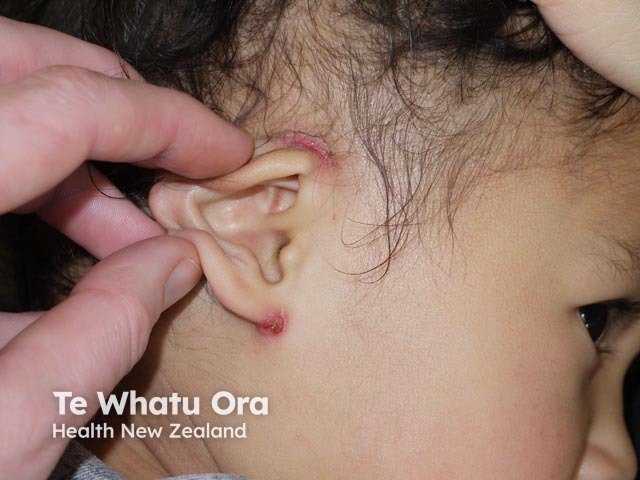
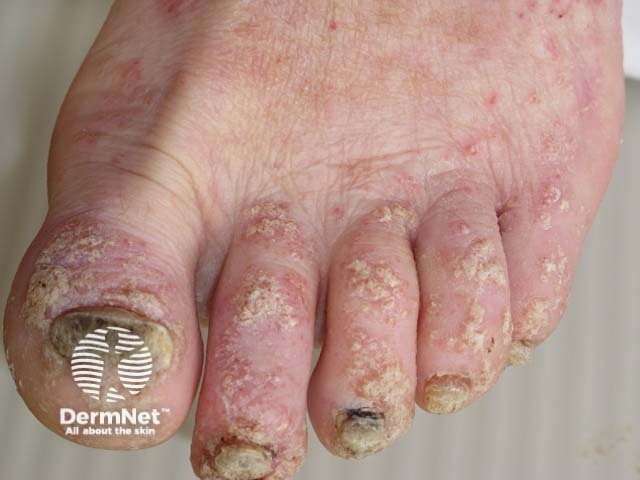
Scabies
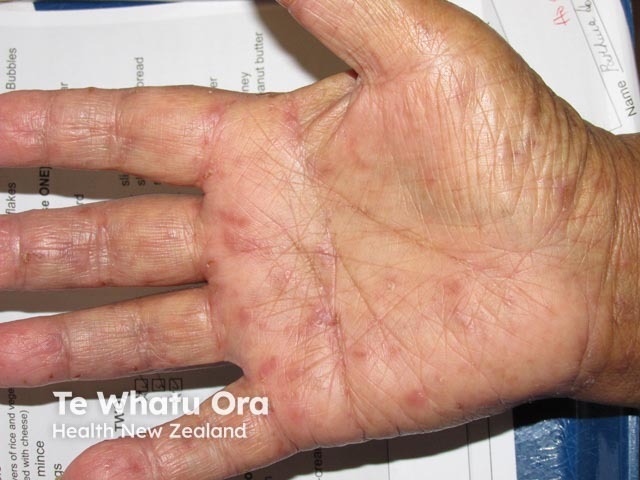
Scabies
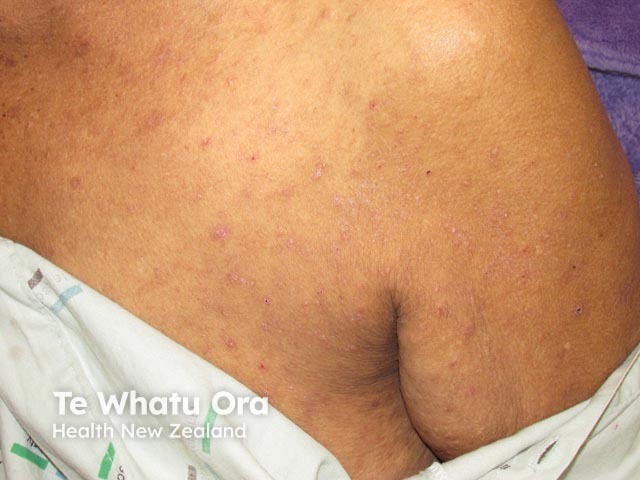
Scabies
Transient acantholytic dermatosis / Grover disease
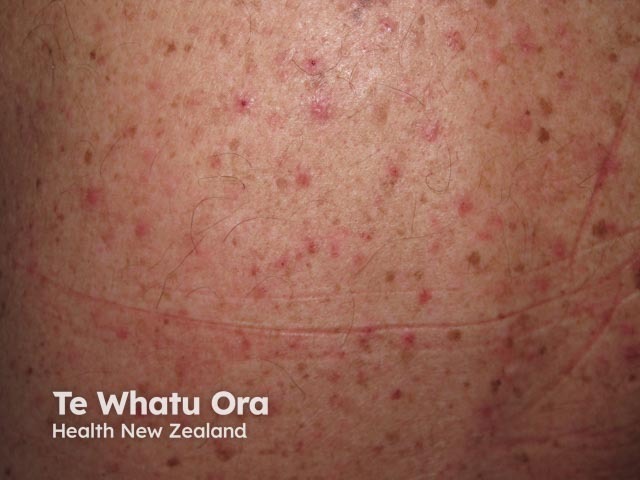
Transient acantholytic dermatosis
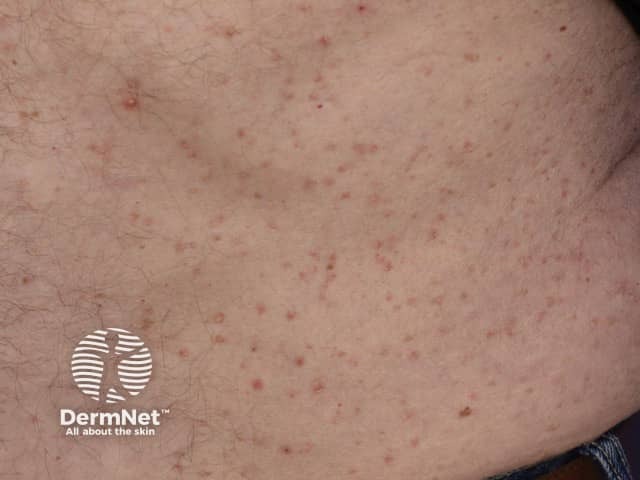
Transient acantholytic dermatosis
Transient acantholytic dermatosis
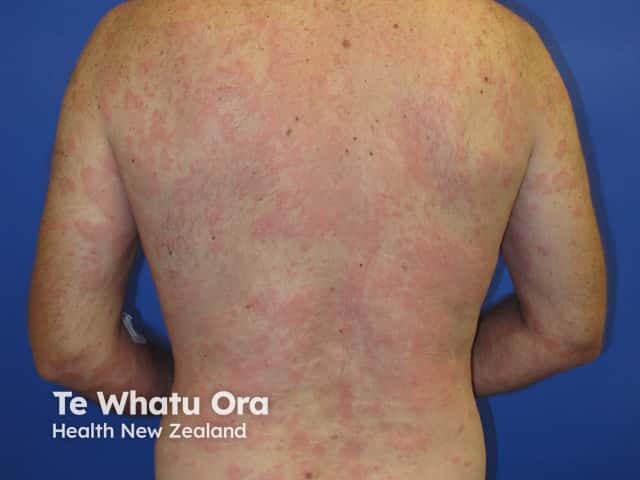
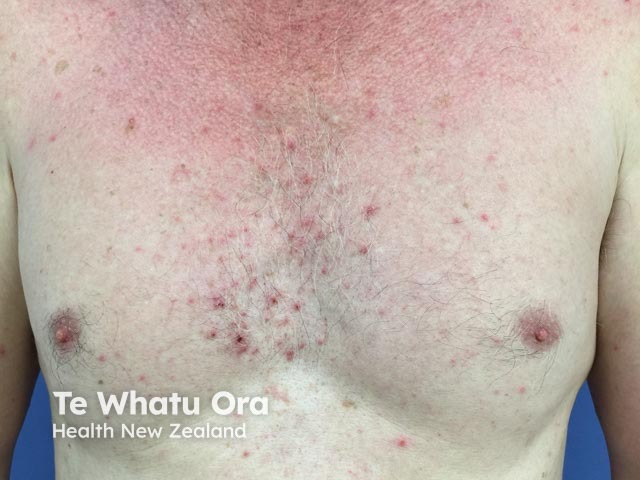
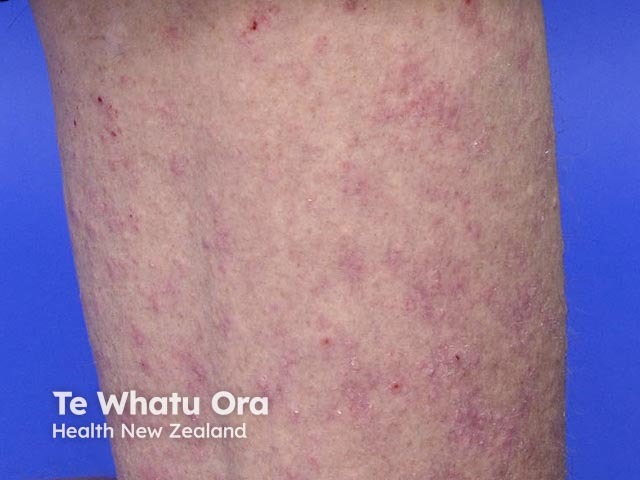
Spontaneous urticaria
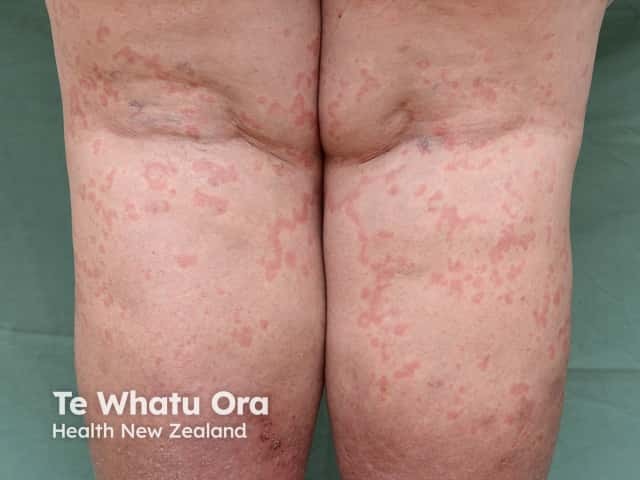
Spontaneous urticaria
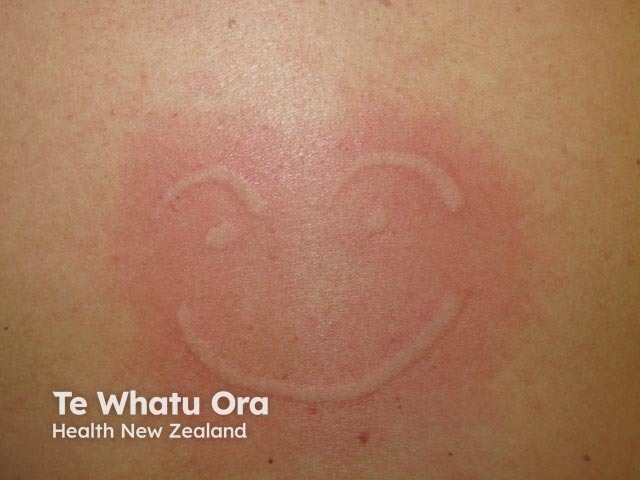

Dermographism
Urticaria
Urticaria
Urticaria
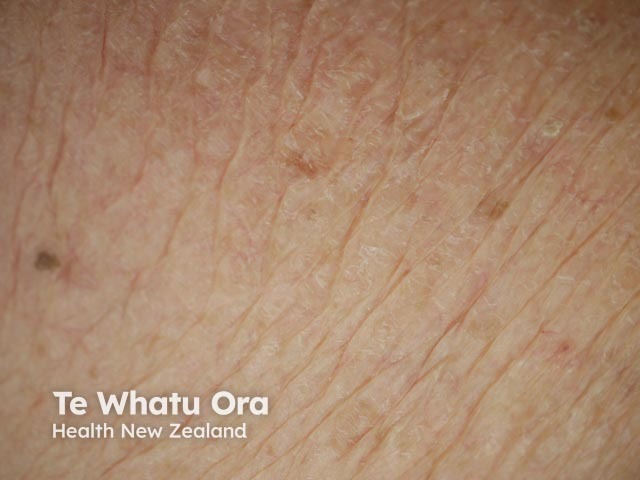
Xerosis
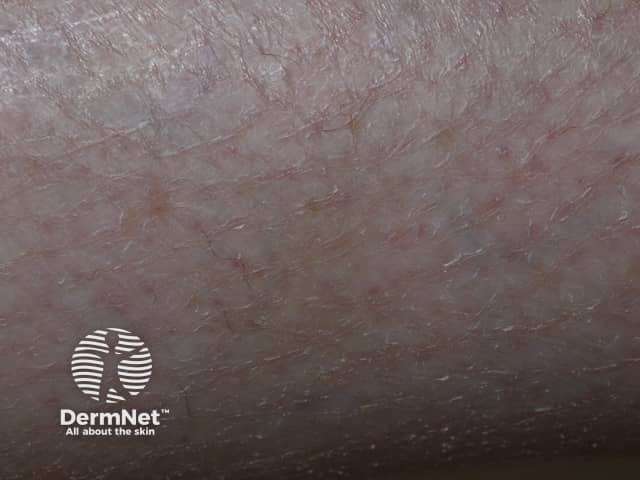
Xerosis
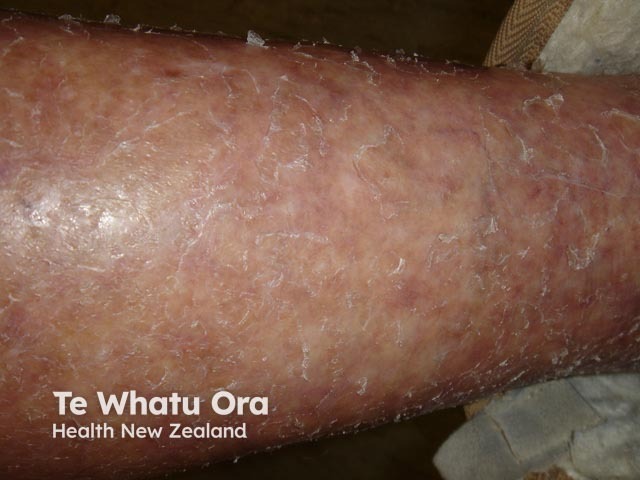
Xerosis
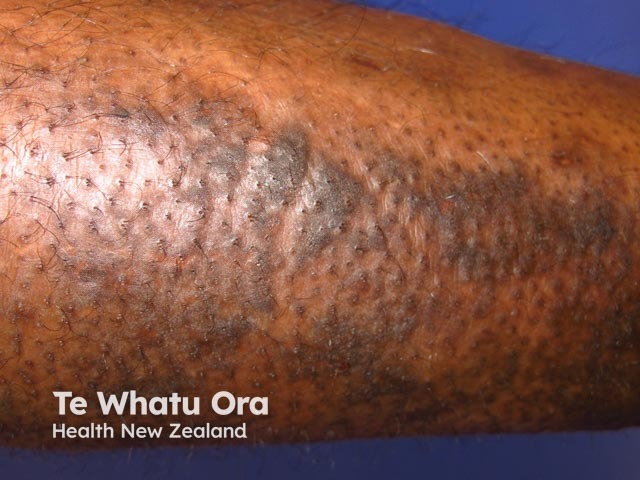
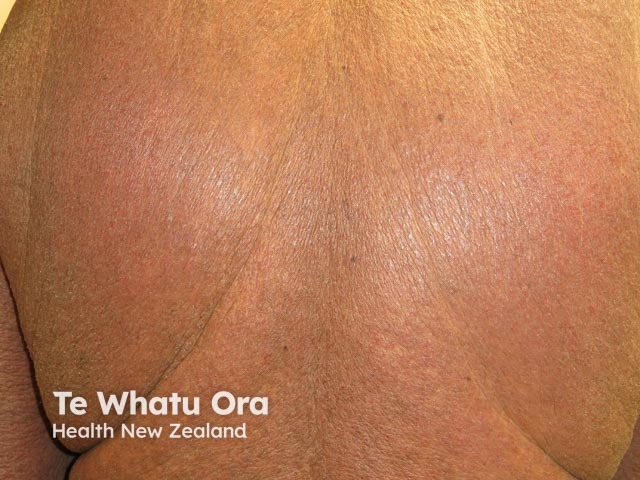
May have secondary lesions due to scratching: erosions, purpura, lichen simplex and secondary infection. Localised itch is often neuropathic/neurogenic. If scalp itchy, look carefully for head lice and their egg cases.
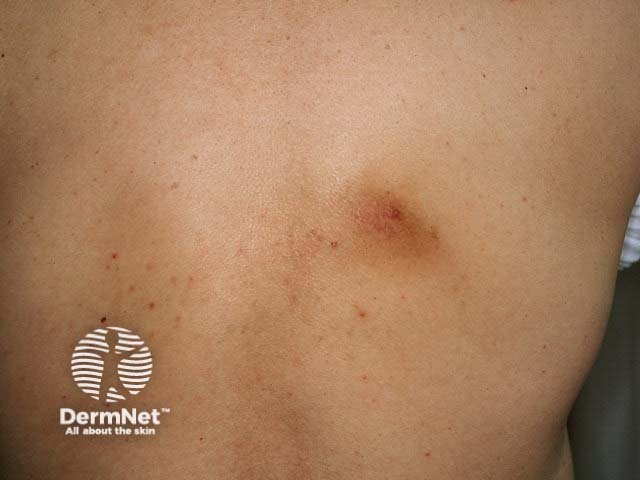
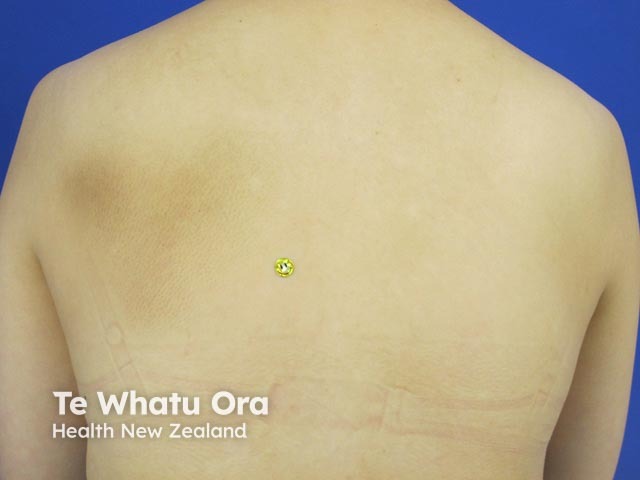
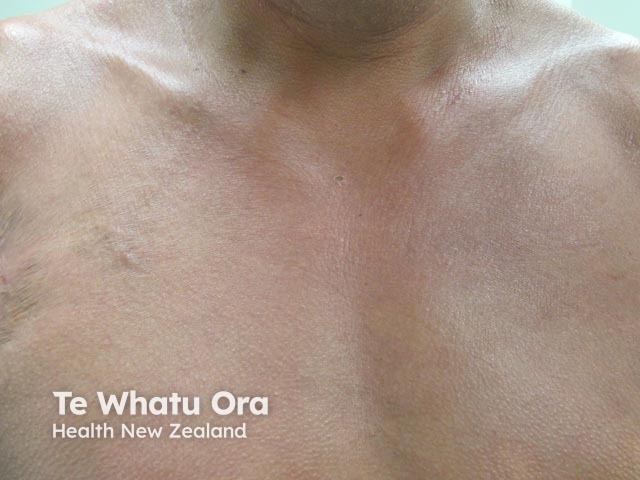
Notalgia paraesthetica
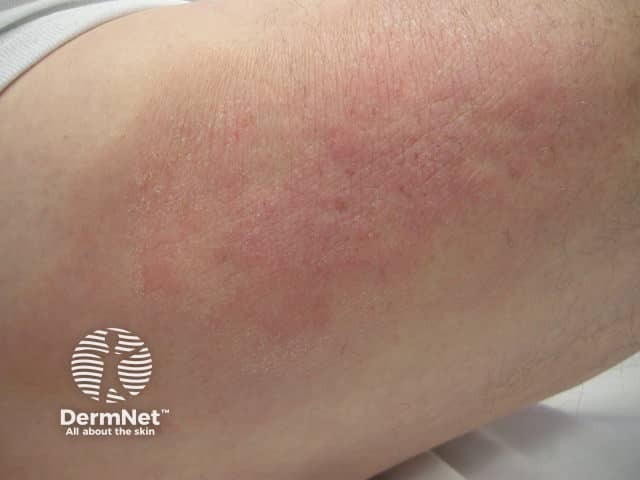
Meralgia paraesthetica
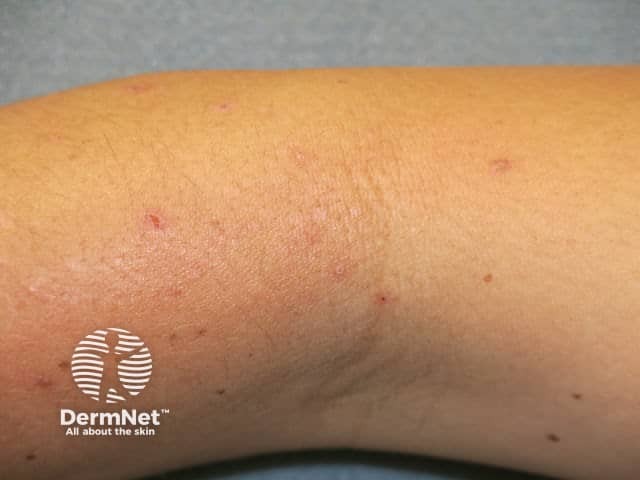
Lichenification from scratching
Examine carefully for scabietic burrows.
Systemic disease
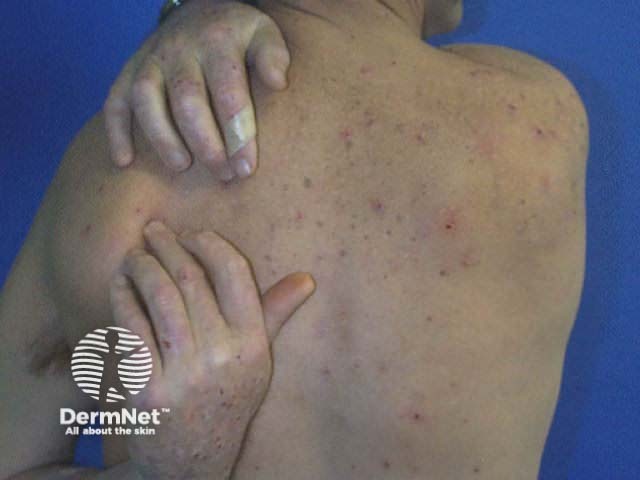
Renal pruritus
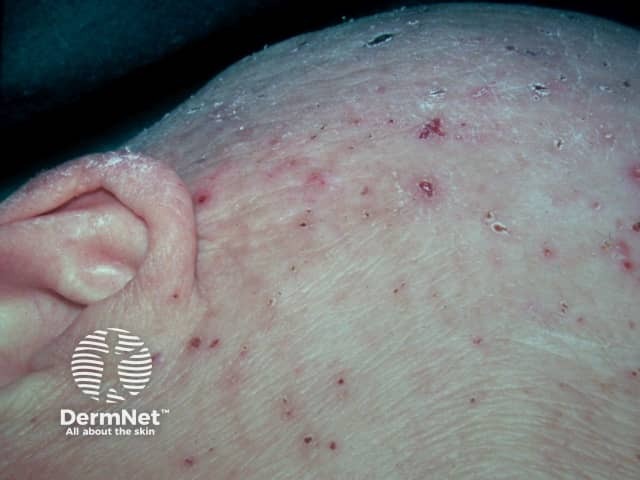
Breast cancer
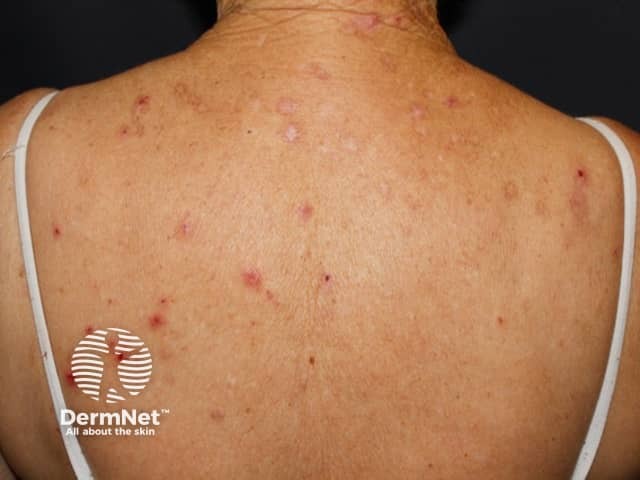
Iron deficiency