Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Dr Nick Turnbull, Dermatology Registrar, Auckland and Greenlane Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand, 2010; DermNet Update July 2021. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell.
Viral hepatitis is inflammation of the liver due to infection with viruses from the hepatotrophic family: hepatitis A (HAV), hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV), hepatitis D (HDV), and hepatitis E (HEV). Many other viruses can also cause hepatitis; this review will focus on the skin changes associated with infection by the known hepatotrophic viruses.
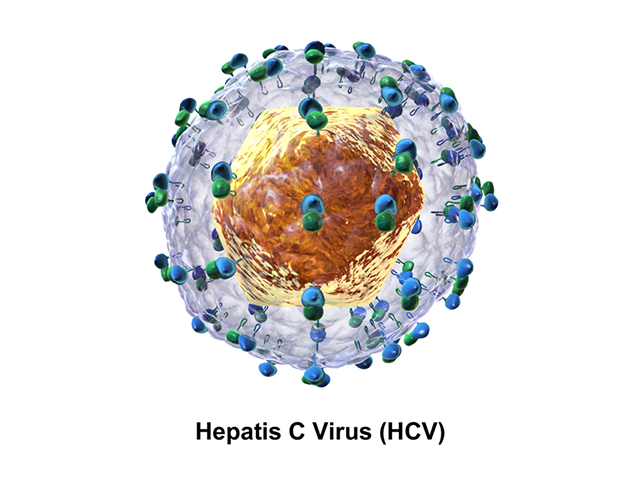
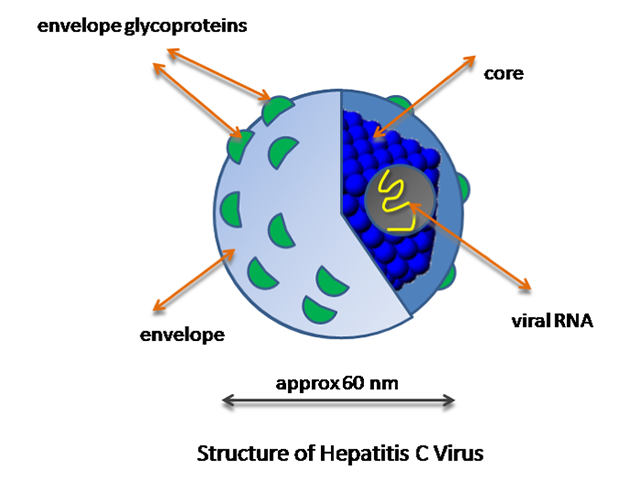
Viral hepatitis due to hepatotrophic viruses can be divided into acute and chronic forms.
Skin changes are found in up to 17% of HCV-positive patients.
HDV is usually a co-infection in patients with chronic HBV accelerating progression to early liver failure.
HEV is the most common cause of acute viral hepatitis worldwide, although it is often asymptomatic or only mildly symptomatic with jaundice following a prodromal phase. It can progress to chronic infection in immunocompromised patients.
Skin changes in acute viral hepatitis can be nonspecific such as the itch secondary to jaundice. Chronic viral hepatitis can cause progressive liver failure and skin changes due to cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Skin changes seen with viral hepatitis can be due to:
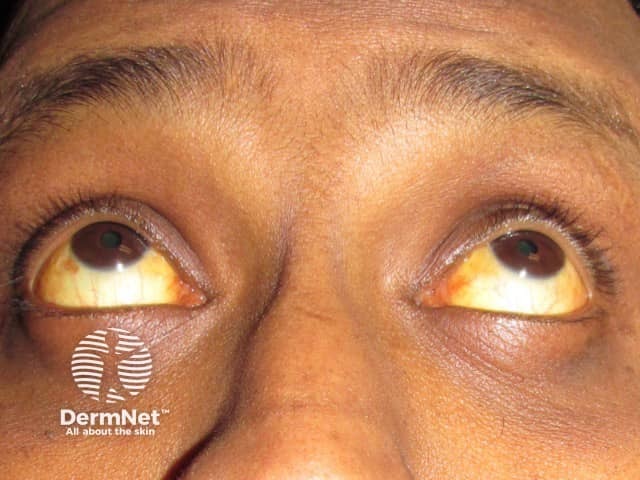
Jaundice
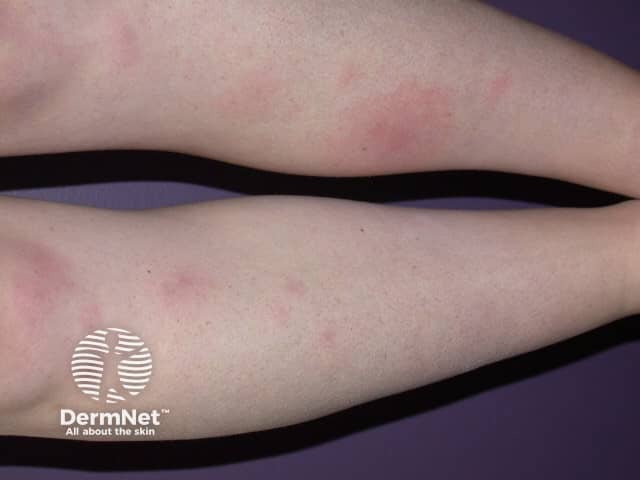
Erythema nodosum
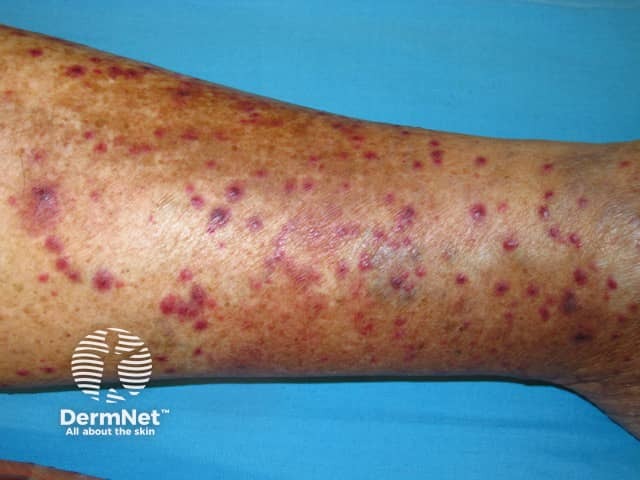
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
At least 20% of patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV or HCV develop skin changes, only a few of which are diagnostic of viral hepatitis.
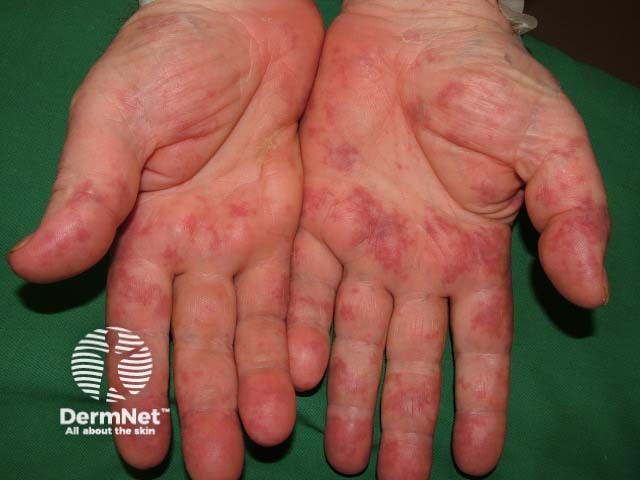
Vasculitis due to cryoglobulinaemia
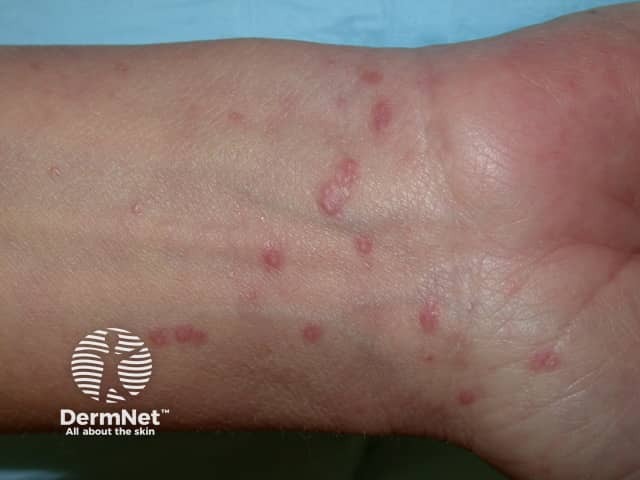
Lichen planus
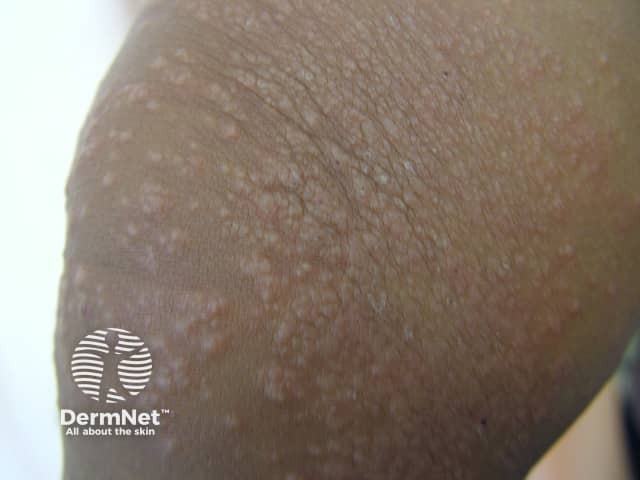
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome
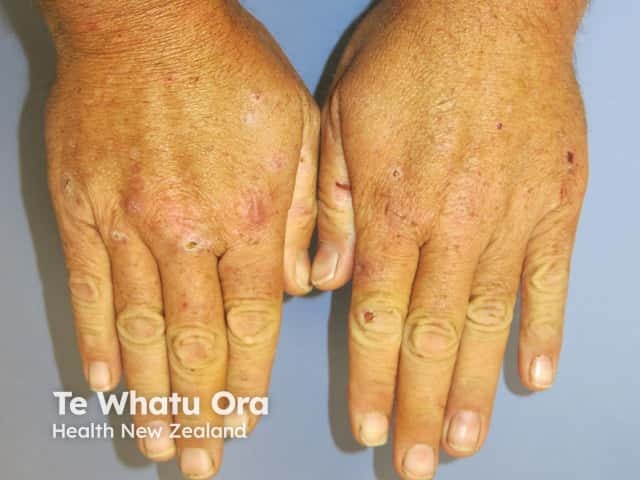
Porphyria cutanea tarda
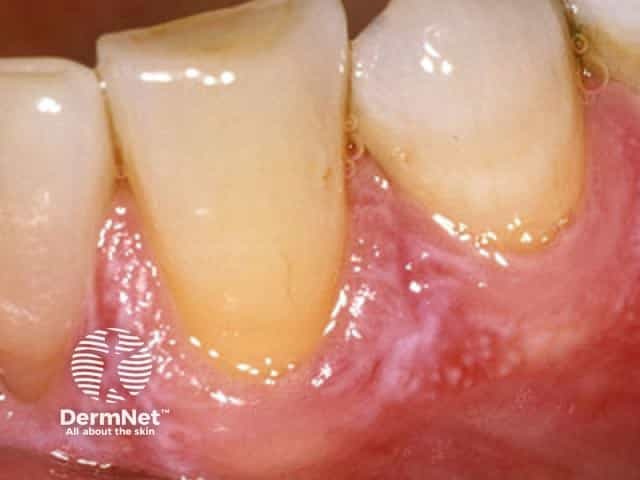
Erosive oral lichen planus
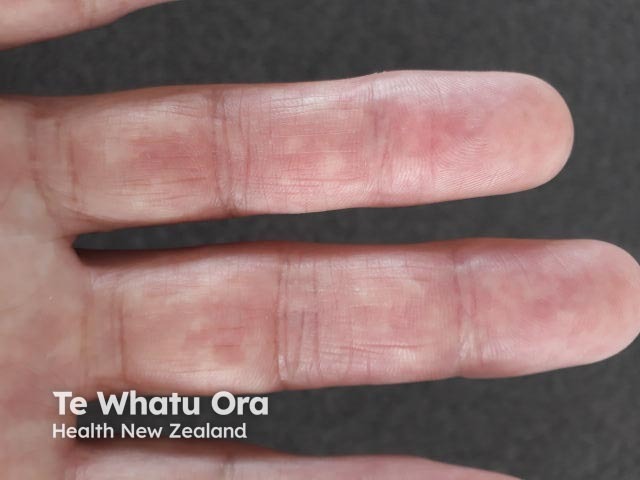
Bier spots
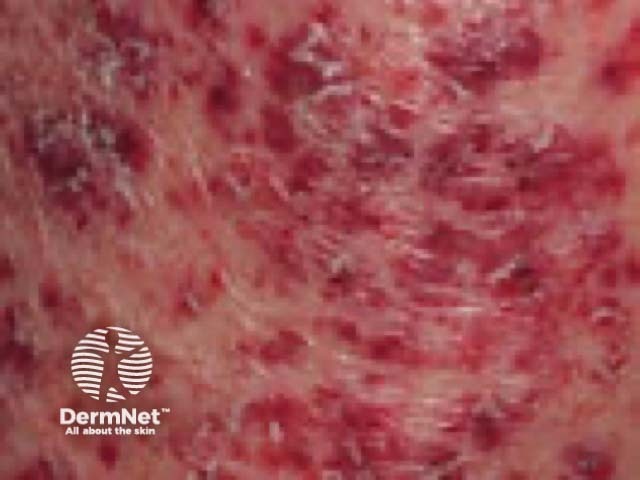
Purpura
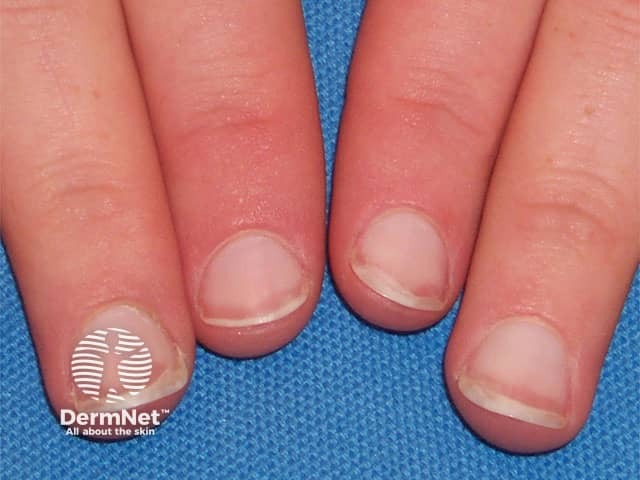
Terry nails