Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth, including the inner aspect of the lips, cheeks, gums, tongue, and throat. It is a type of mucositis. It can be acute or chronic, mild or serious.
Inflammation of the vermilion of the lips is known as cheilitis, inflammation of the tongue is glossitis, inflammation of the gums is gingivitis, and inflammation of the back of the mouth is pharyngitis.
Stomatitis results in pain, stinging, and soreness. It can present with:
These can lead to dehydration and malnutrition.
Stomatitis can be due to injury, infection, allergy, systemic or skin disease. Most commonly, it is due to:
Some of the causes of stomatitis are listed in the table below.
Causes of stomatitis |
|
|---|---|
Bacterial infection |
|
Fungal infection |
|
Viral infection |
|
Systemic disorder |
|
Drugs |
|
Physical irritation |
|
Contact stomatitis |
|
Immunobullous disesase |
|
Other |
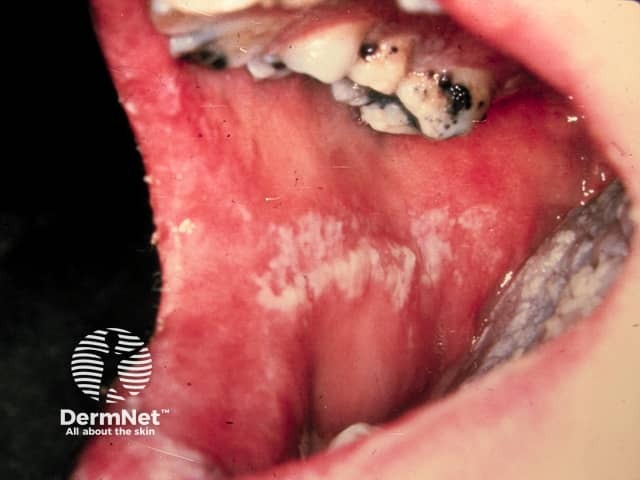
Oral candidiasis
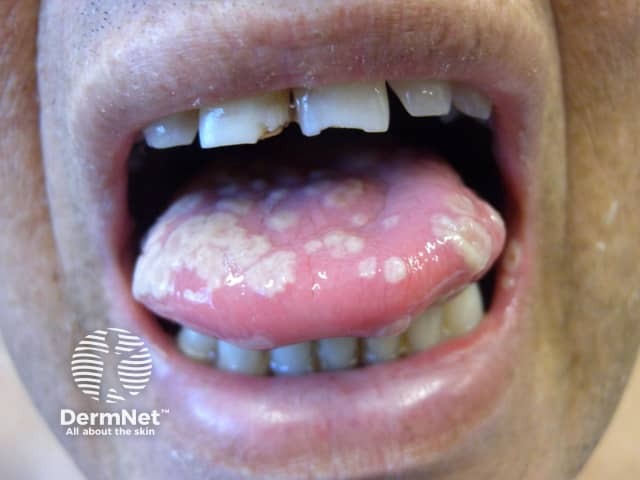
Severe herpes simplex infection
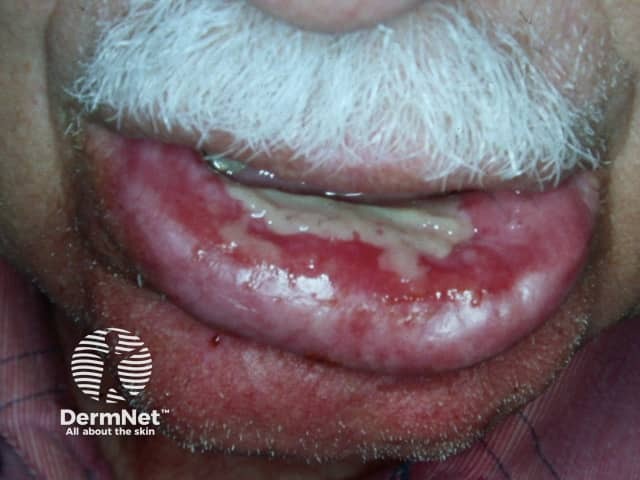
Radiation stomatitis
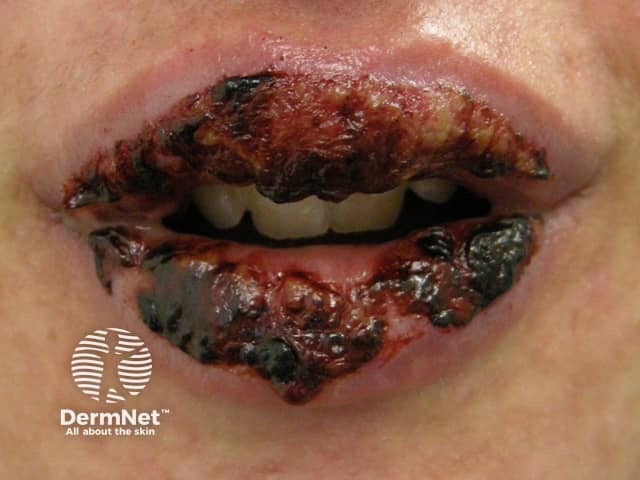
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
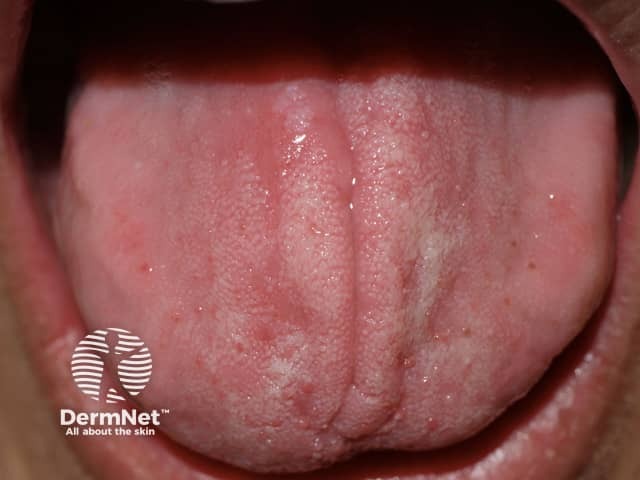
Contact allergy
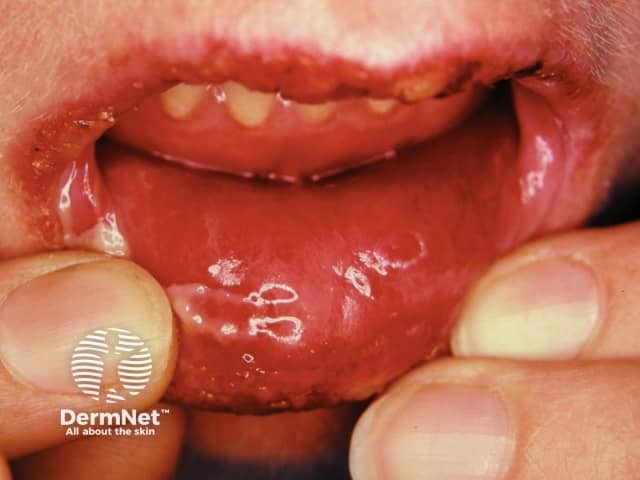
Erosive lichen planus
Relevant investigations depend on the likely cause of stomatitis and whether it is accompanied by other symptoms internally or skin rashes.
They may include:
Treatment for stomatitis depends on the cause. If it is due to allergy to a medication, the medication must be promptly stopped. However, it may be necessary to continue a causative medication when stomatitis arises as an expected adverse reaction to chemotherapy.
Infections may require specific treatment such as antibiotics for streptococcal pharyngitis, topical antifungal or oral antifungal agent for candida infection.
Nutritional deficiencies should be identified and corrected, for example, folic acid can reduce methotrexate-induced stomatitis.
Immunobullous diseases may be treated with systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive treatments.
Symptomatic treatment may include: