Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Authors: Dr Scott Barker, Dermatology Registrar, New Zealand, 2006. Updated: Dr Sarah Elyoussfi, Dermatology Registrar and Dr Ian Coulson Consultant Dermatologist. East Lancashire NHS Trust, United Kingdom. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. November 2021.
Introduction
Demographics
Causes
Mucocutaneous features
Other organ involvement
Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses
Treatment
Outcome
Sjögren syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disease that mainly affects secretory glands of the eyes and mouth, reducing production of tears and saliva (sicca symptoms) and resulting in dry eyes (called keratoconjunctivitis sicca) and dry mouth (xerostomia).
Many patients with Sjögren syndrome also have features of other autoimmune diseases, such as systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. In this case, they are said to have an overlap syndrome or SS is said to be secondary to the other autoimmune disorder (termed secondary SS). The diagnosis is primary SS when other conditions are not present.
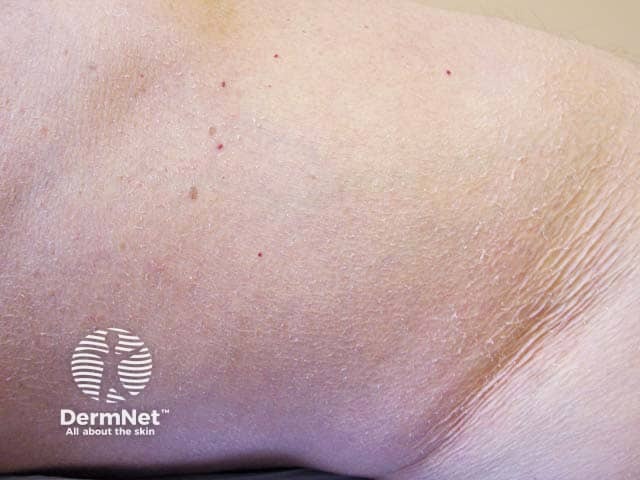
Xerosis in Sjogren syndrome
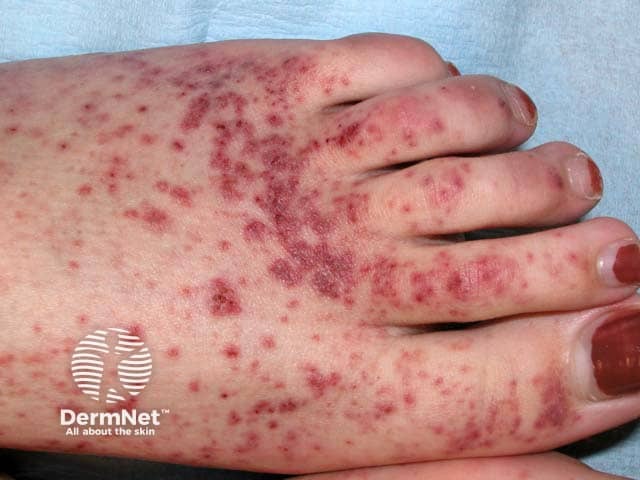
Small vessel vasculitis in Sjogren syndrome
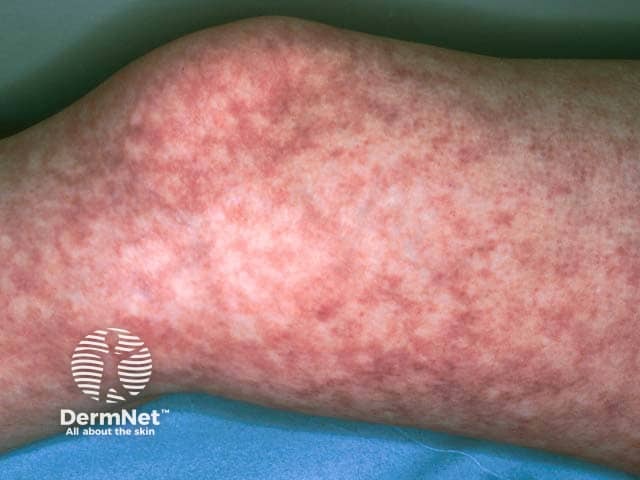
Cryoglobulinaemic livedo in Sjogren syndrome
Primary Sjögren syndrome is 9 times more common in females than males. Anyone can develop it, but it is especially common in older females in the fifth and sixth decades of life. Up to 2% of older females have been found to have primary SS.
The prevalence of primary SS in the population ranges from 0.01–0.09%.
Sjögren syndrome does not have a known cause. One theory is that viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus may play a role in triggering SS in people with a genetic background that predisposes them to SS. Once the condition has been triggered, lymphocytes infiltrate the secretory glands. This is a slow, low-grade inflammatory process that damages the cells of the glands and thus impairs gland function.
Variants of certain genes such as IRF5-TNPO3, STAT4, and IL12A may cause dysregulation in both adaptive and innate immunity that is important for the development of primary Sjögren syndrome.
Dry mouth may develop very gradually over years. Oral symptoms include:
The common skin manifestation of Sjögren syndrome include:
Other skin changes reported in primary Sjögren syndrome include:
Extra-glandular manifestations occur in approximately 50% of patients; constitutional features include:
Systemic manifestations can mimic malignancy.
Gastrointestinal system involvement is rare. Dryness may inflame the lining of the oesophagus (oesophagitis) and the stomach (atrophic gastritis).
Dry cough, due to dryness of the small airways.
Up to 60% of people with Sjögren syndrome will develop at least one episode of arthralgia or arthritis at some stage. Arthritis does not usually result in erosion of joint structures or deformity.
Involvement of the kidneys (interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis) is more common if Sjögren syndrome is present as part of an overlap syndrome with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Risk factors associated with development of lymphoma include:
Primary Sjögren's syndrome vasculitis can damage the kidneys, lungs, nerves, and joints. Involvement of internal organs is more likely if the vasculitis is associated with cryoglobulinaemia.
Ataxic neuropathy may occur.
Sjögren syndrome is usually a clinical diagnosis, and can be supplemented by the following tests:
This test measures the wetting of a standardised piece of filter paper applied between the bulbar and lachrymal conjunctiva. If less than 5 mm in 5 minutes, it is confirmatory of SS.
Minor salivary glands are biopsied from the inside of the lip, pathology shows a lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Sialography, salivary scintigraphy, and high resolution ultrasound can confirm salivary gland pathology. Sialometry is positive if there is less than 1.5 ml of saliva in 15 min unstimulated.
Autoantibodies blood tests can be useful.
Diagnostic criteria have been proposed with high sensitivity but limited specificity.
Most sufferers have a chronic condition but their symptoms can be alleviated. They have a lower than average incidence of cardiovascular disease. Prognosis can be worsened by the development of lymphoma, neurological disease, and vasculitis affecting the kidneys and lungs.