Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Hon A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, December 2016.
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is a cytokine associated with inflammatory disorders of the skin, joints, and gastrointestinal tract.
The most active tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (anti-TNF drugs) are monoclonal antibodies targeted against TNF-alpha (TNFα). Anti-TNFα drugs control inflammation in inflammatory skin diseases, arthritis, and bowel disease. They were among the first biologic agents on the market.
Anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies include:
Other drugs with activity against TNF include:
Natural compounds acting against TNF include:
The anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies are used mainly in the treatment of severe chronic plaque psoriasis.
They are also used for other severe inflammatory skin diseases when conventional therapies have failed. Examples include:
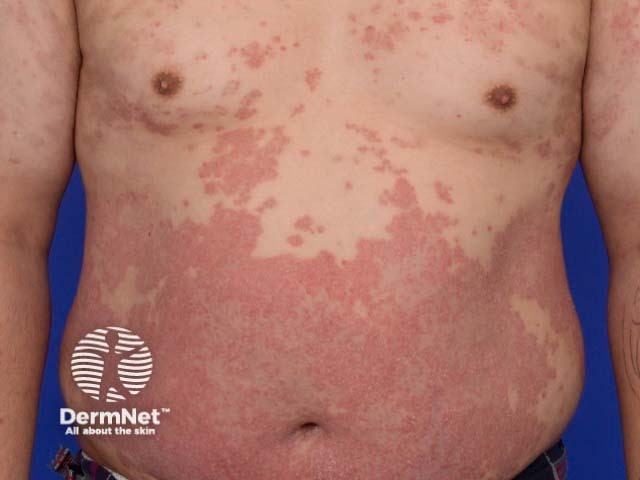
Severe psoriasis
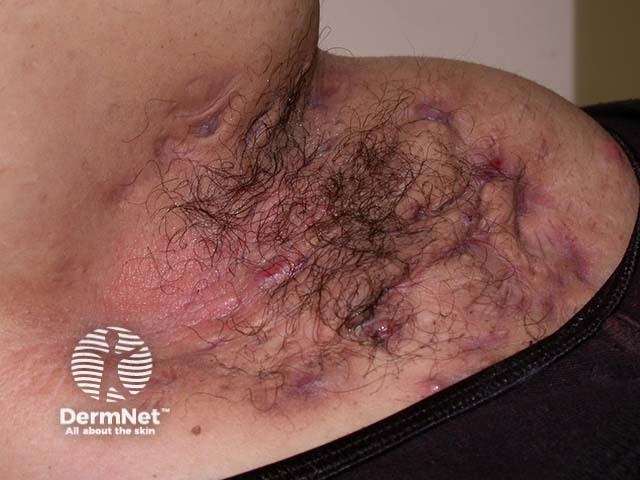
Hidradenitis suppurativa
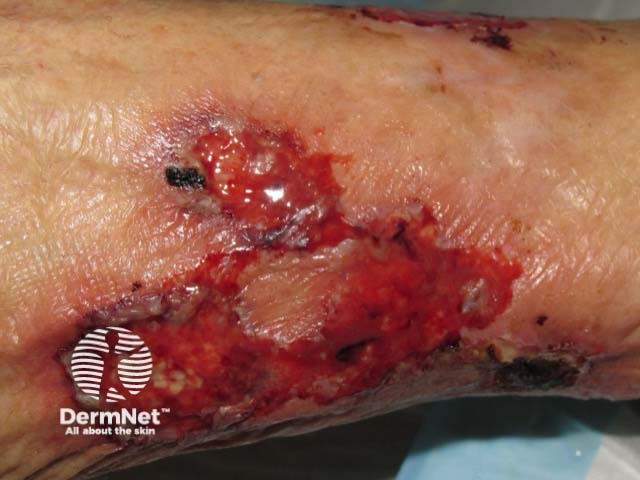
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Anti-TNF biologics are given by injection. They can sometimes cause injection site reactions or infusion reactions.
They should be avoided in patients with severe heart failure.
The main risk of anti-TNF therapy is reduced immunity to bacterial, fungal, viral, and parasitic infections, including:
They may also increase the risk of developing skin cancers and autoimmune diseases, including demyelinating conditions.
Anti-TNF medicines can lose their effect over time, possibly because of the induction of antibodies against them.
Paradoxically, anti-TNF drugs can sometimes have dermatological side effects, such as:
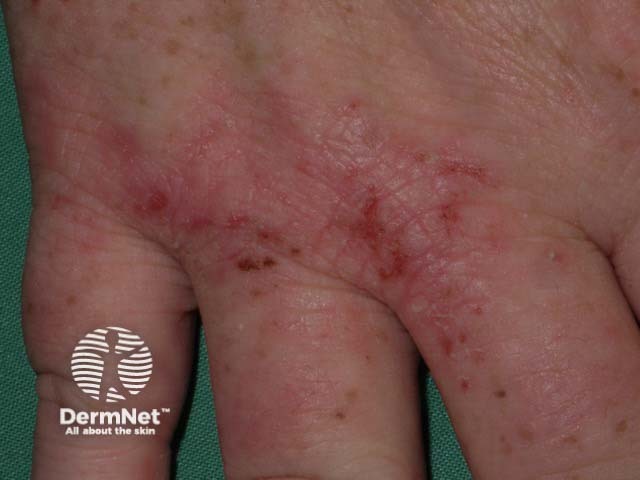
Hand dermatitis
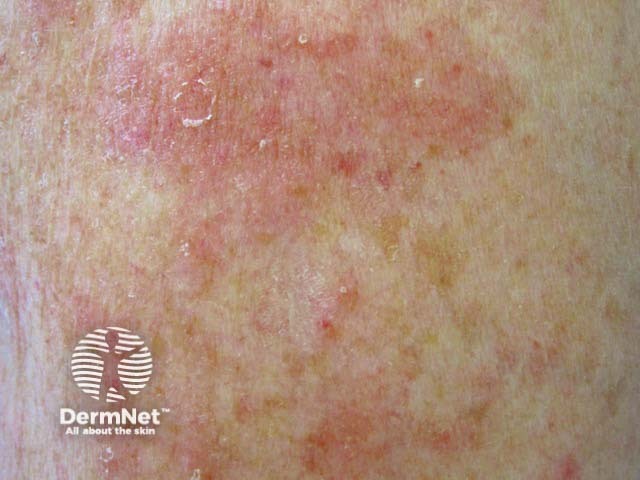
Nummular dermatitis
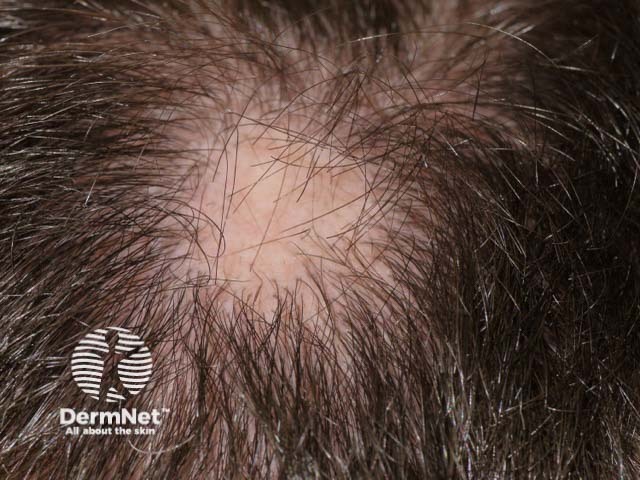
Alopecia areata
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).