Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Last Reviewed: July, 2025
Author(s): Nancy Huang (MBChB), DermNet Medical Writer, New Zealand (2025); Dr Cindy Lam, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia (2023)
Peer reviewed by: Dr Vidette Wong, Specialist doctor, United Kingdom (2025)
Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson (2025)
Edited by the DermNet content department
Introduction
Uses
Contraindications and precautions
Benefits
Disadvantages
Side effects and risks
Upadacitinib (RINVOQ®) is an oral, second-generation selective Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor used for atopic dermatitis (eczema). It targets the JAK1 enzyme and modulates the immune response.
Upadacitinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in January 2022 for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Upadacitinib has since received approval for this indication by other regulatory bodies, including the MHRA (UK), TGA (Australia), and Medsafe (NZ).
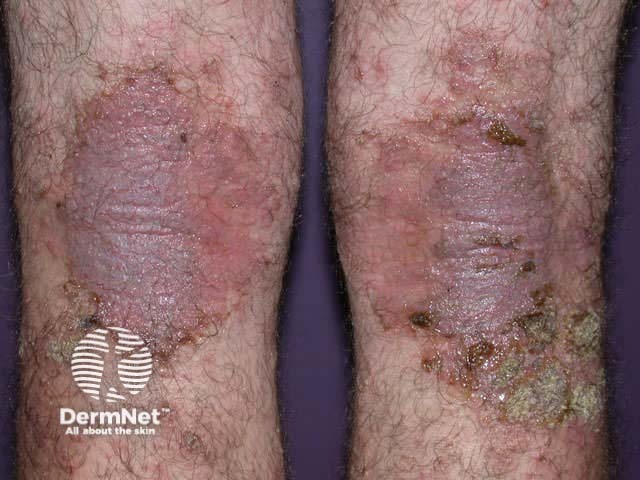
Severe atopic dermatitis unresponsive to topical therapies, phototherapy, and methotrexate - candidate for a JAK inhibitor
More images of atopic dermatitis
In dermatology, upadacitinib is used for adults and adolescents (12 years and older) with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who are candidates for systemic therapy.
Off-label dermatological uses include:
Dermatological uses described in small studies include:
Other licensed uses:
As with other JAK inhibitors, ensure vaccination status is updated prior to commencing upadacitinib, including vaccination for herpes zoster (recombinant zoster vaccine).
Live vaccinations should not be given during or just before starting treatment. Live vaccines include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), typhoid, bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), yellow fever, varicella zoster, rotavirus, and Japanese encephalitis.
See: Immunisation in immunosuppressed dermatology patients.
Upadacitinib is available as 15 mg modified-release oral tablets. Tablets can be taken with or without food and should be swallowed whole.
In adults and adolescents (≥12 years old and weighing ≥40 kg), the dosing for the treatment of atopic dermatitis is 15 mg once daily. If response is inadequate, consider increasing the dose to 30 mg once daily.
If elderly (age ≥65), or with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15-30mL/min/1.73m2), or taking a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor (eg, ketoconazole, clarithromycin) the maximum dose is 15 mg once daily.
Treatment should be ceased if:
Upadacitinib is generally well tolerated with a favourable benefit-risk profile.
Common side effects:
Uncommon side effects:
Rare side effects:
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).