Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Treatments Autoimmune/autoinflammatory
Author: Anoma Ranaweera, Medical Writer, Auckland, New Zealand. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. December 2019.
Introduction
Introduction - psoriasis
How it works
How to use
How long to use
Contraindications
Warnings and precautions
Use in specific populations
Potential drug interactions
Possible side effects
Pharmacological class-associated adverse effects
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel are topical medications for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in adult patients 18 years or older [1,2]. The brand names of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate are Daivobet® 50/500 ointment and Daivobet® 50/500 gel. The New Zealand marketing authorisation holder is LEO Pharma. Calcipotriol is also called calcipotriene. In some countries, the brand name for the combination product is Dovobet®.
Daivobet® ointment and Daivobet® gel are available in New Zealand with a doctor’s prescription and are fully funded by PHARMAC.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder characterised by circumscribed, red, scaly plaques.
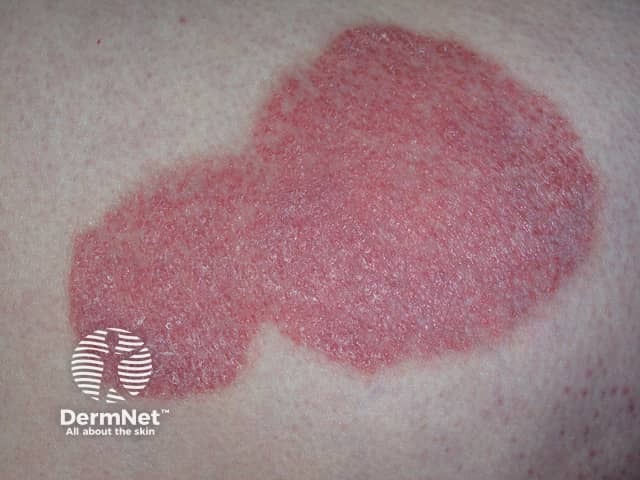
Chronic plaque psoriasis
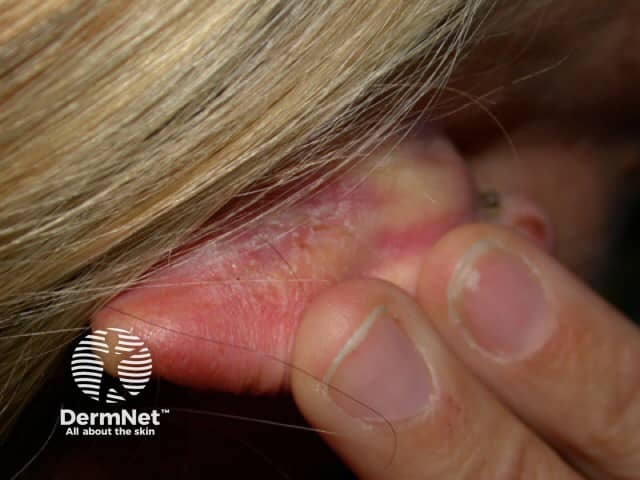
Psoriasis of the scalp
The mechanism of action of the ingredients has been studied independently as well as in combination [1–3].
Calcipotriol hydrate is a synthetic vitamin D analogue.
Betamethasone dipropionate is a potent synthetic topical corticosteroid.
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel combine the pharmacological effects of calcipotriol and betamethasone dipropionate. The combination of the two medications has a specially designed formulation that works to both reduce inflammation and to treat the scaling associated with psoriasis.
Each gram of both calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel contains 50 mcg of calcipotriol and 500 mcg of betamethasone dipropionate [1–3].
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel are applied topically to the affected areas once daily. The recommended treatment period is 4 weeks.
After this period, calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment may be used according to need under medical supervision [1,2]. The maximum daily and weekly doses should not exceed 15 g and 100 g, respectively.
For the application of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate gel, an amount between 1 g and 4 g per day is sufficient for the treatment of the scalp (4 g corresponds to one teaspoon). In order to achieve optimal effect, it is recommended that the hair and affected areas of the skin are not washed immediately after application of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate gel. Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate gel should remain on the affected area overnight or during the day. The gel can also be used on psoriasis on the trunk and limbs, especially for hairy skin.
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel are not recommended for use in children and adolescents below the age of 18 years, due to the lack of data on safety and efficacy [1–3].
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel should not be used:
The treated skin areas should be protected from sunlight and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, for example, by wearing sun protective clothing, as sunlight inactivates calcipotriol.
Additional topical corticosteroids should not be used in areas treated with calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel [1–3].
If a dose of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel is missed, apply it as soon as you remember. If it is time to apply the next dose, the missed dose is skipped. Do not apply a double dose.
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel is generally used for 4 weeks but can be used for up to eight weeks on a physician recommendation. The physician may recommend repeat treatments depending on the response to the first treatment.
The main contraindication to calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel is hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients [1–3].
It should not be used for acute types of psoriasis such as generalised pustular psoriasis or erythrodermic psoriasis.
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel should also not be used on the face or skin folds, or for skin affected with:
Before using calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel, a patient should inform the treating physician of the following circumstances:
Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria have been observed with the use of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and is more likely if recommended doses are exceeded (maximum daily dose 15 g; maximum weekly dose 100 g) [1–3].
In view of the risk of hypercalcaemia secondary to excessive absorption of calcipotriol when there is extensive skin involvement, calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel should not be used on more than 30% of the body surface area.
If hypercalcaemia or hypercalciuria develops, treatment should be discontinued until parameters of calcium metabolism have normalised.
Serum calcium and renal function should be monitored at 3-monthly intervals during periods of usage of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel.
Systemic absorption of a topical corticosteroid, such as betamethasone dipropionate, can rarely produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for clinical glucocorticosteroid insufficiency during treatment or upon withdrawal of the topical corticosteroid.
Factors that predispose a patient to HPA axis suppression include:
Systemic effects of topical corticosteroids may also include Cushing syndrome, hyperglycaemia, and glucosuria. Local side effects from topical corticosteroids include:
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel contain butylated hydroxytoluene (E321), an excipient within the excipient polyoxypropylene stearyl ether, which may cause local skin reactions (eg, contact dermatitis), or irritation to the eyes and mucous membranes [1,2].
Visual disturbance has been reported with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient presents with symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be referred to an ophthalmologist for evaluation of possible causes which may include cataract, glaucoma, or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy, which have been reported after use of systemic and topical corticosteroid [1–3].
The phototoxic effects of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel have not been systematically studied in psoriasis patients undergoing phototherapy or exposed to sunlight. Treated skin areas should be protected from sunlight and UV radiation (using sun-protective clothing or sunscreens), particularly where exposure may be considerable for reasons such as occupation [1–3].
The safety and efficacy of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel in children less than 18 years of age have not yet been established in formal trials [1,2].
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, children under the age of 12 years are at particular risk of systemic adverse effects when they are treated with topical corticosteroids, including growth retardation [1–3].
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women [1,2].
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel. However, calcipotriol has been shown to be fetotoxic and betamethasone dipropionate has been shown to be teratogenic in animals when given systemically.
Betamethasone is excreted into breast milk. It is unknown if topical application of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce significant quantities of this corticosteroid in human breast milk. There are no data on the excretion of calcipotriol in breast milk [1,2].
Application of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment to the breast area should be avoided to prevent possible direct ingestion by infants. Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel should only be used during lactation if the potential benefits clearly outweigh the potential risks.
After applying calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment or gel to their skin, mothers should wash their hands thoroughly prior to handling their infant child.
Safety has not been established in patients with renal impairment. Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel are contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment [1–3].
Safety has not been established in patients with hepatic impairment. Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel are contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [1–3].
Possible effects of betamethasone in combination with calcipotriol on fertility have not been investigated in animals. Studies of the oral administration of calcipotriol in rats have shown no impairment of male and female fertility [1,2].
No interaction studies have been carried out with calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel [1,2]. There is no experience with concurrent use with other systemic therapy for psoriasis or with phototherapy.
Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment should not be used concurrently with calcium or vitamin D supplements, or with drugs that enhance the systemic availability of calcium.
The clinical trial programme for calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel has so far included more than 2,500 patients and has shown that approximately 10% of patients can be expected to experience a non-serious adverse effect [1,2].
The only common (< 1/10) adverse event observed in treated recipients was pruritus and skin exfoliation.
Adverse effects in < 1/100 treated recipients associated with the use of calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate ointment and gel in clinical trials included [1–3]:
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Potential adverse reactions of calcipotriol include application site reactions such as:
Local reactions can occur after topical use of betamethasone dipropionate, especially during the prolonged application, including:
Systemic reactions due to prolonged use of topical corticosteroids over large areas of the skin include:
Healthcare professionals are advised to report all suspected adverse reactions to the New Zealand Pharmacovigilance Centre.
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).