Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Pustular skin conditions — extra information
Pustular skin conditions
Author: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, September 2015. DermNet Revision September 2021
What are pustules?
Acute mainly pustular generalised eruptions
Acute mainly pustular localised eruptions
Chronic mainly pustular eruptions
What are pustules?
Pustules are smaller than 5–10 mm, and filled with pus, that is, purulent material composed of inflammatory cells (neutrophils).
- Pus can indicate bacterial, fungal or viral infection
- Some pustules are sterile and are due to inflammatory skin disease
This topic provides a differential diagnosis of pustular skin conditions.
- Acute mainly pustular generalised eruptions
- Acute mainly pustular localised eruptions
- Chronic mainly pustular eruptions
Acute mainly pustular generalised eruptions
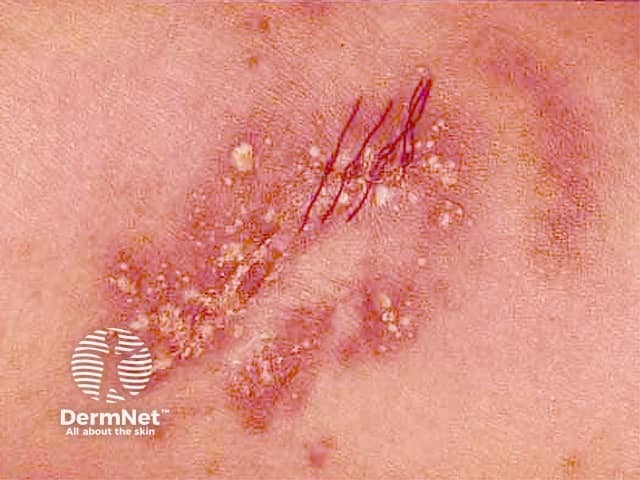
Generalised pustular psoriasis
- Febrile illness
- Annular plaques studded with pustules
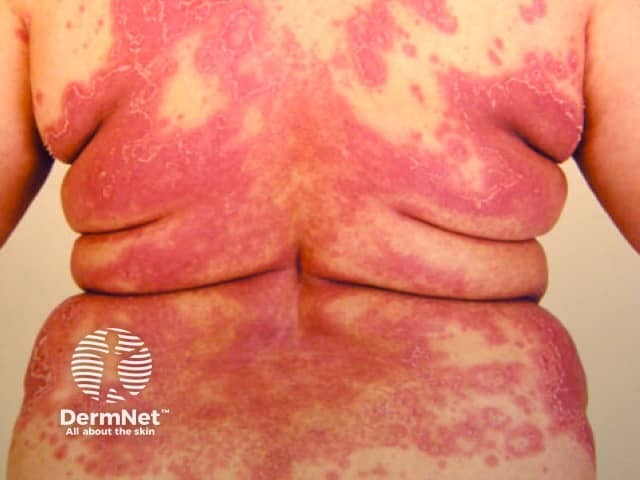
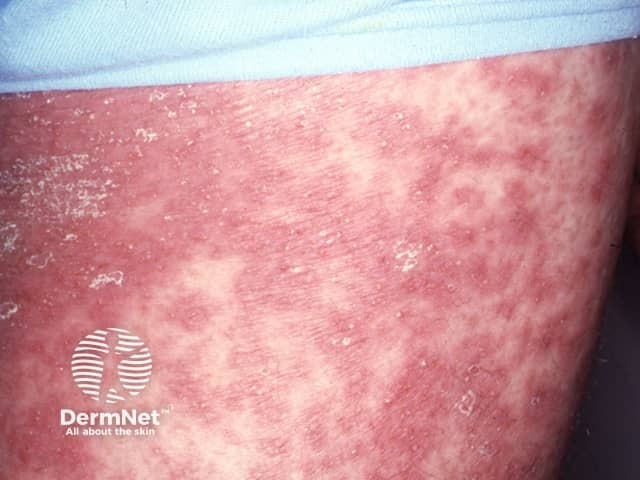
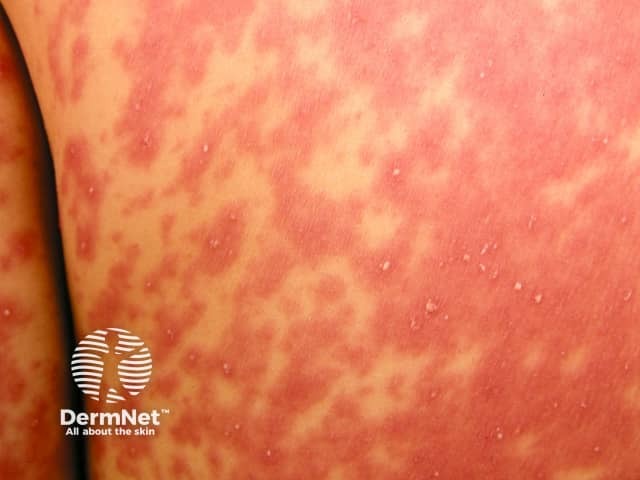
Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis
- Febrile illness
- Drug eruption
- Diffuse superficial pustules
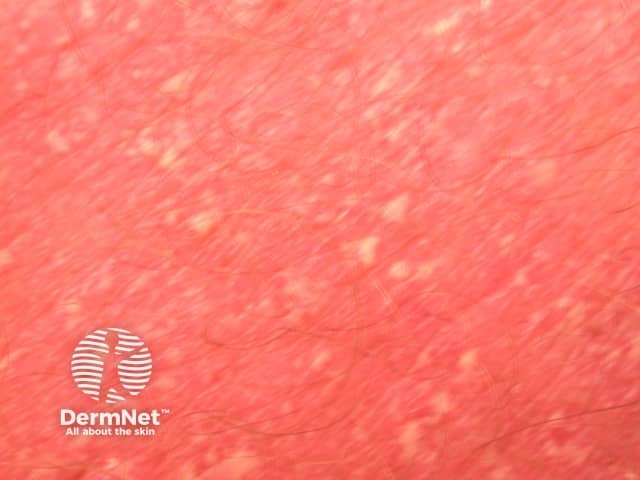
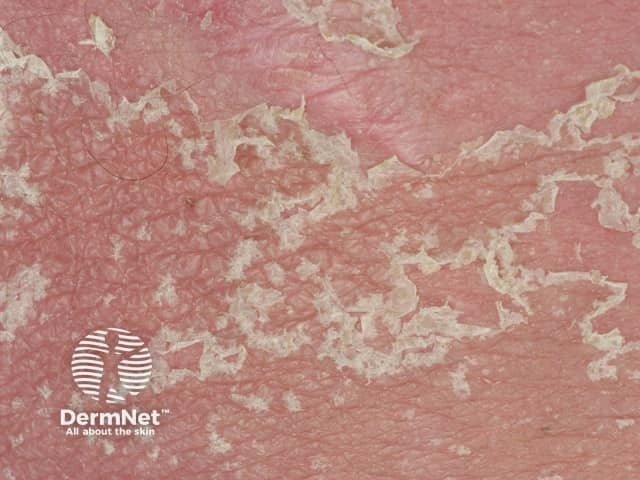
Acute mainly pustular localised eruptions
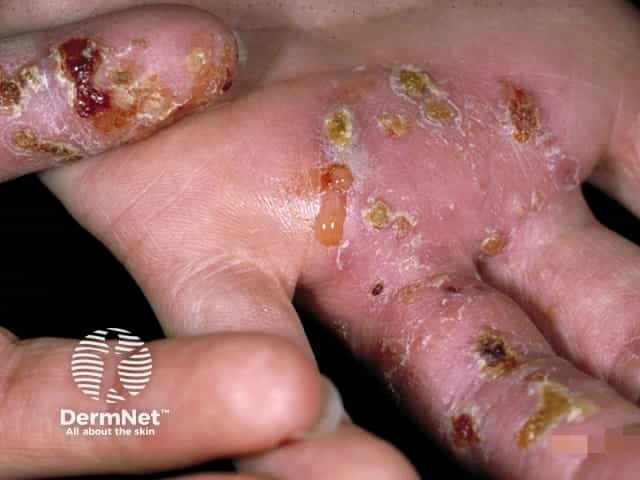
Impetigo
- Rapidly enlarging plaque
- Swab Staphylococcus aureus +/- Streptococcus pyogenes
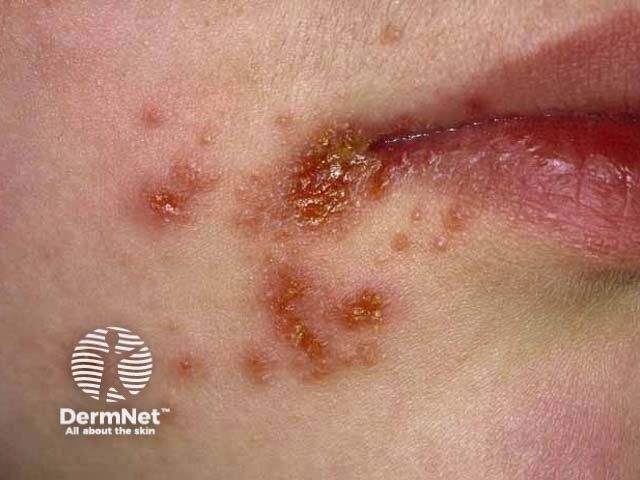
Impetigo
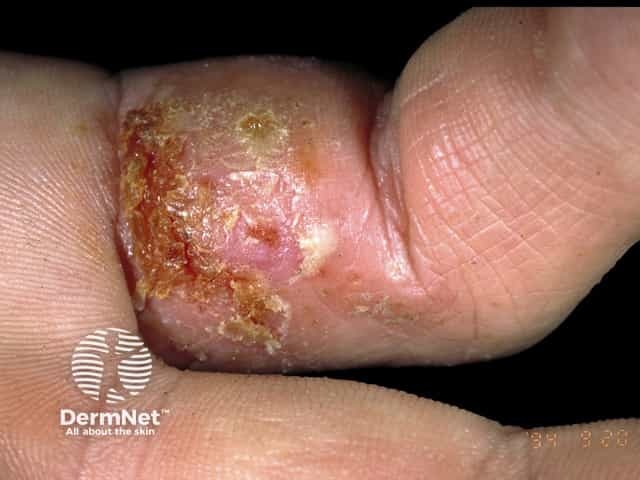
Furunculosis/boil
- Based on hair follicle
- May lead to abscess formation
- Swab Staphylococcus aureus
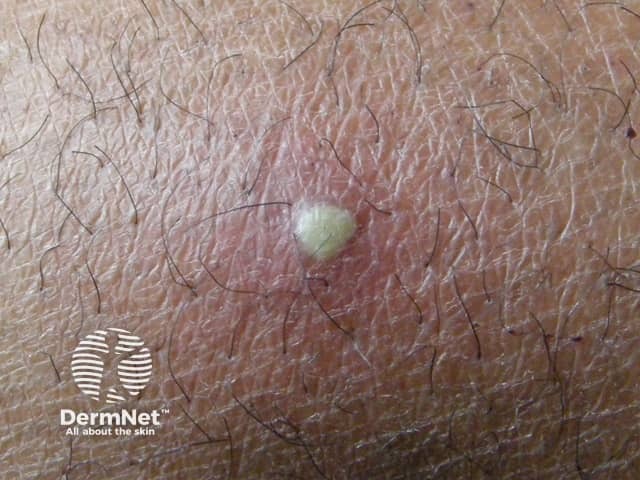
Boil
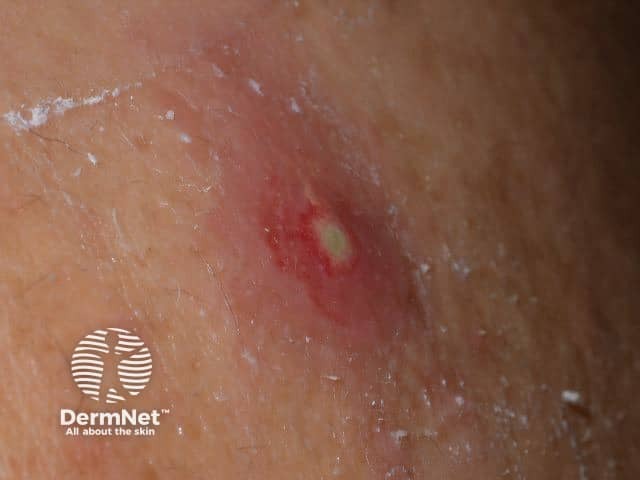
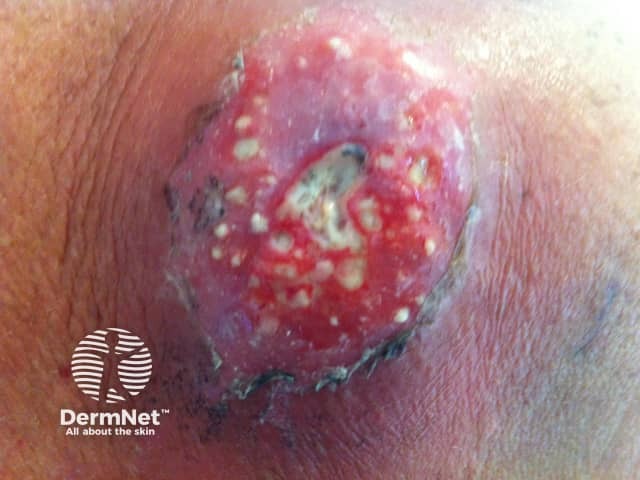
Carbuncle
Folliculitis
- Itchy or painful follicular pustules
- Various types

Superficial bacterial folliculitis
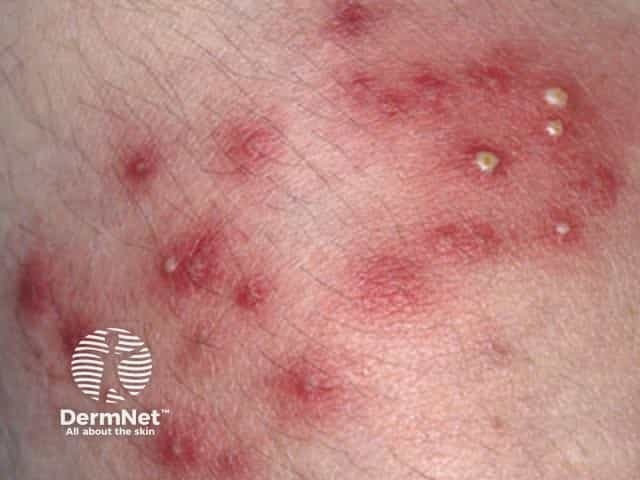
Superficial bacterial folliculitis
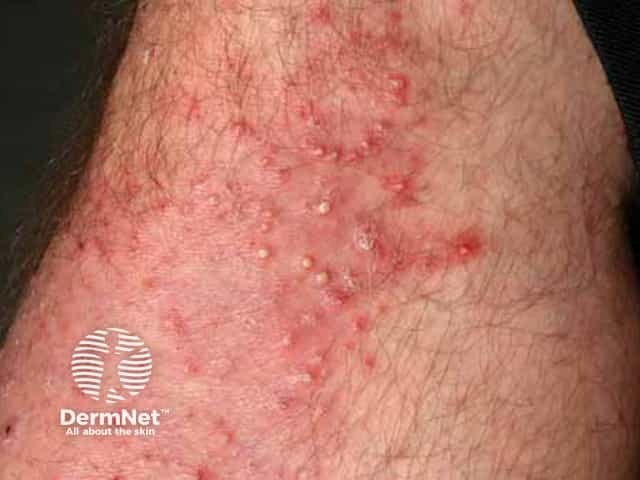
Dermatophyte infection
- Kerion: abscess formation
- Due to zoophilic fungus, eg Microsporum canis
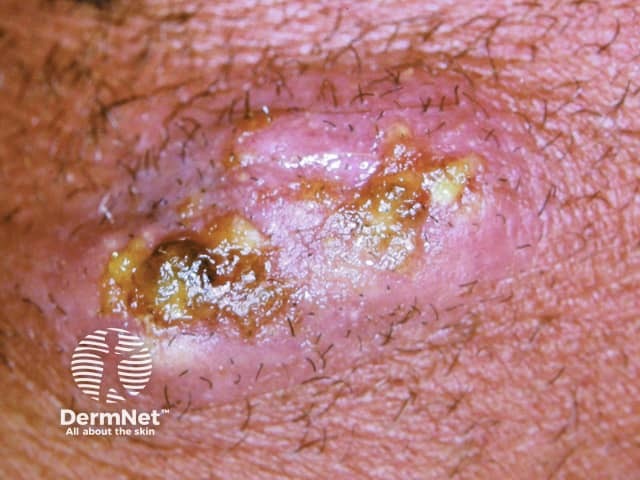
Thrush
- Intertrigo, oral mucosa
- Superficial pustules that dry out easily
- Swab Candida albicans
Candidal intertrigo
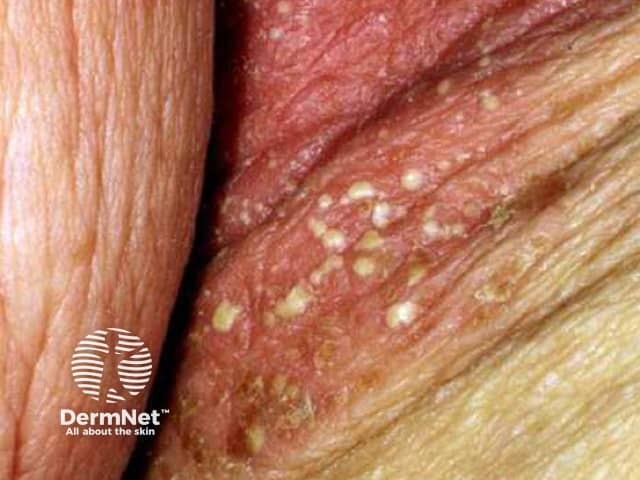
Candida infection
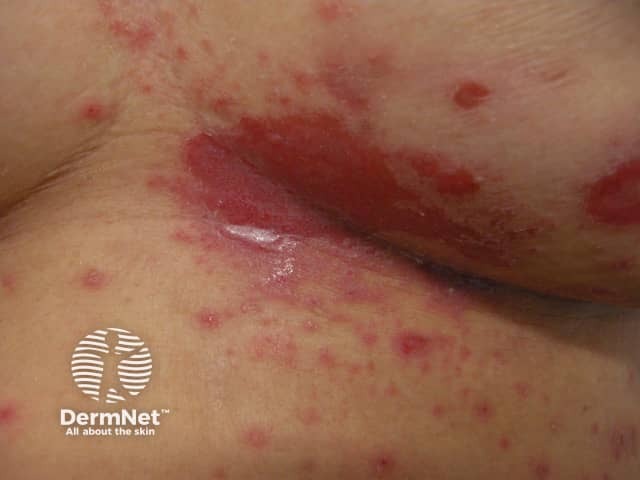
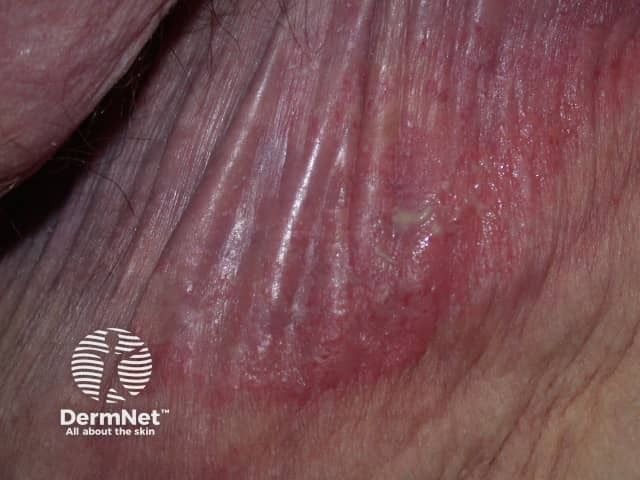
Miliaria
- Sweat rash
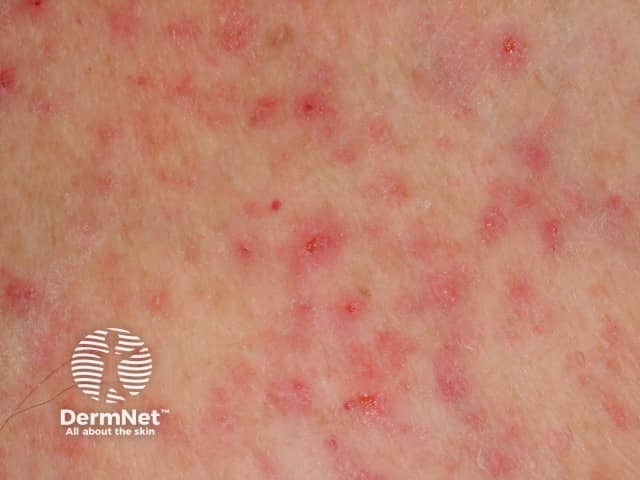
Miliaria
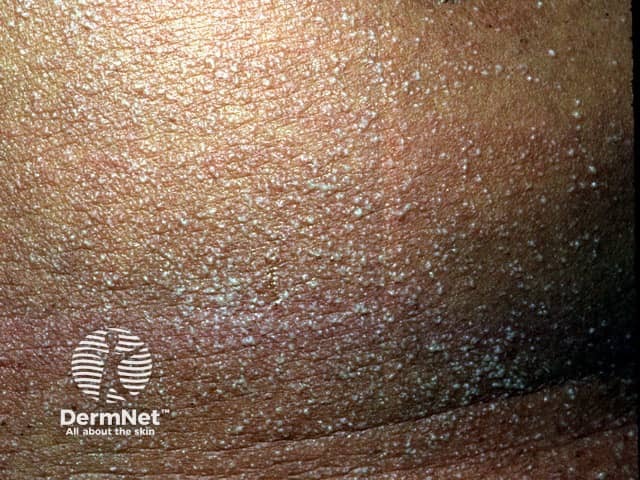
Miliaria
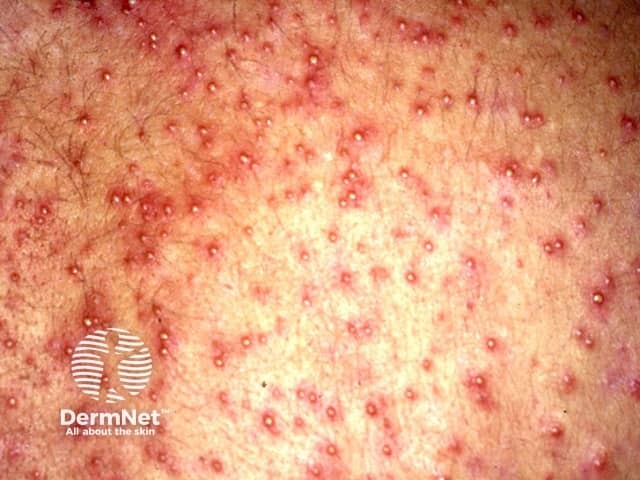
Chronic mainly pustular eruptions
Acne
- Face, neck, upper trunk
- Comedones + inflammatory lesions
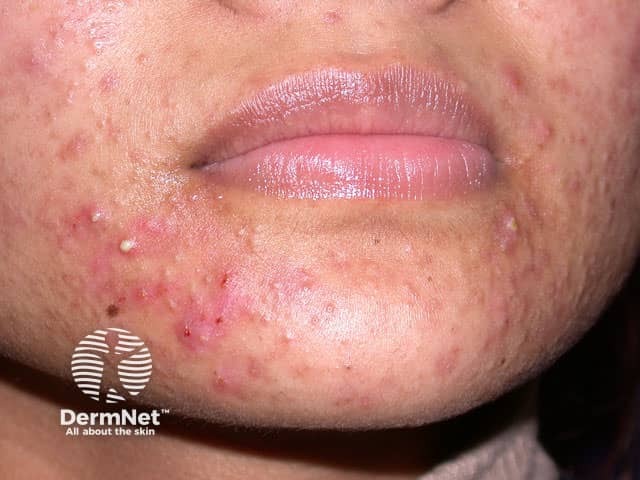
Moderate acne
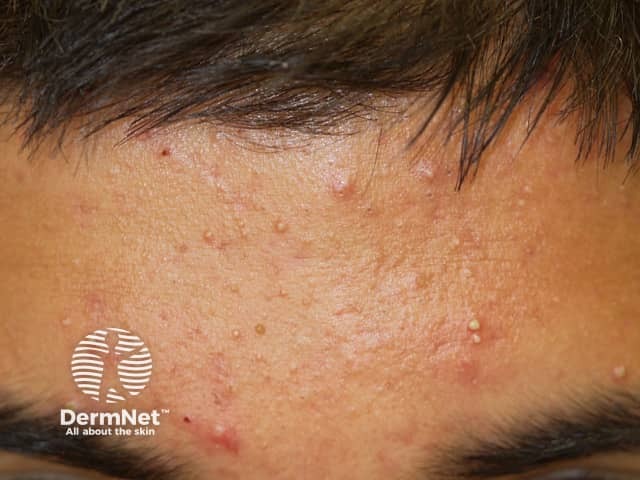
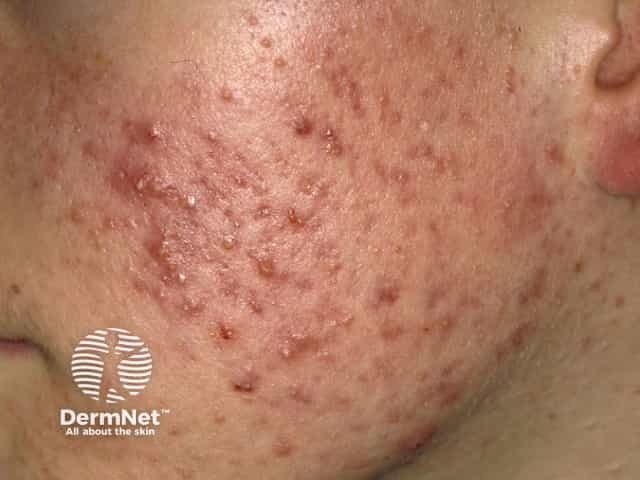
Severe acne
Acneform eruptions
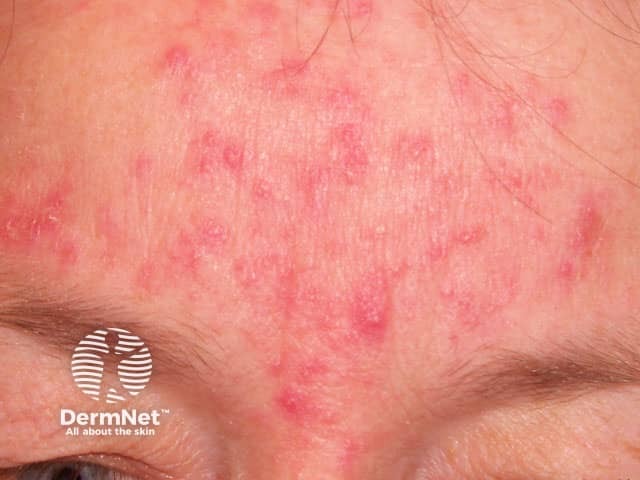
Rosacea
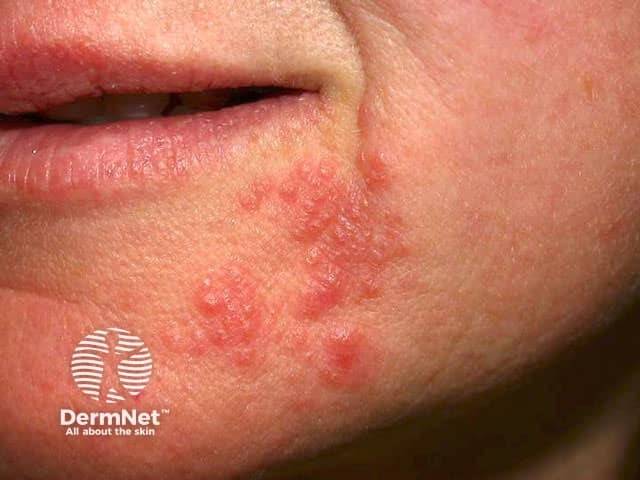
Perioral dermatitis
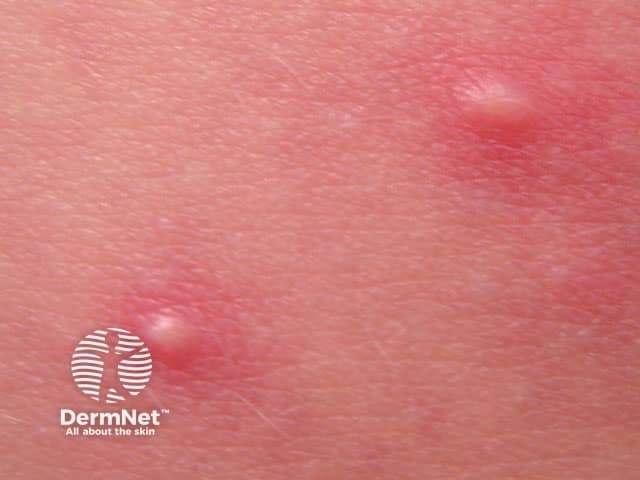
Spa pool folliculitis
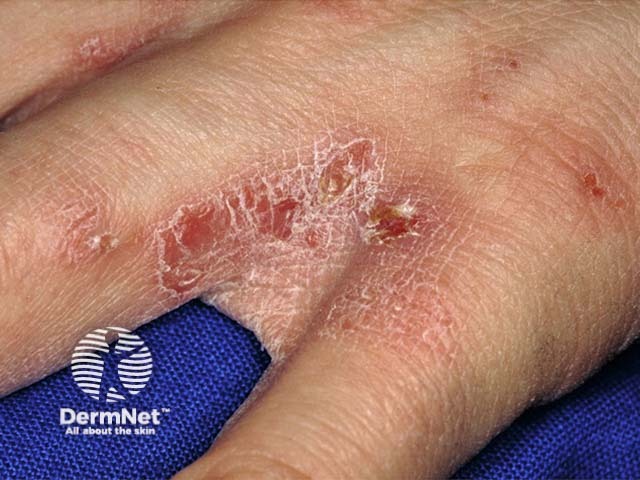
Scabies
- Irregular pustules on hands and feet
- Burrows between fingers, volar wrists
- Papules axillae, groin
- Generalised itchy rash

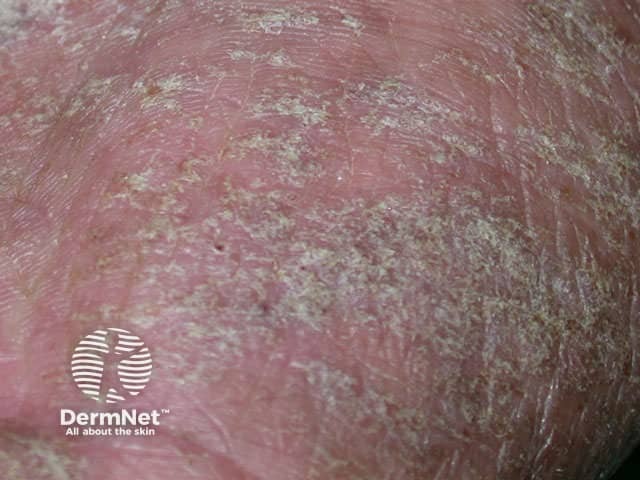
Dermatophyte infection
- Irregular annular plaque with peripheral scale
- Pustules on feet due to Trichophyton interdigitale
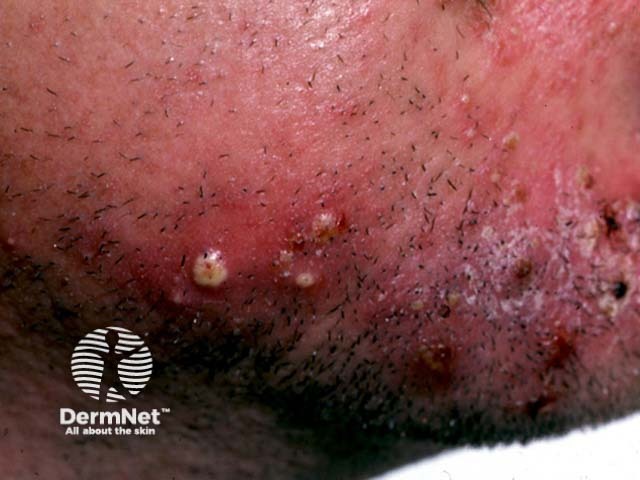
Fungal beard infection
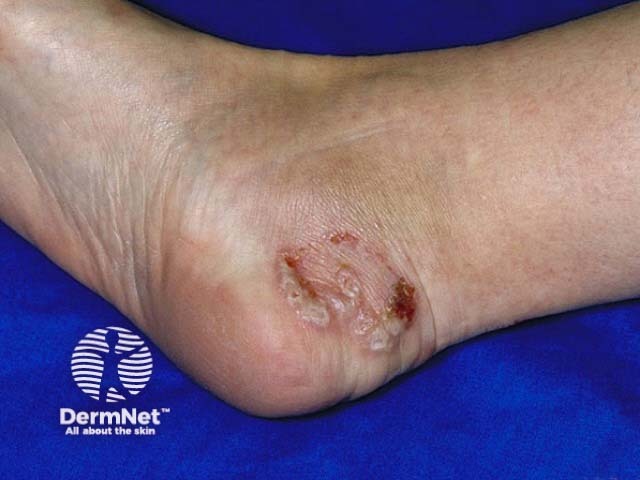
Tinea pedis
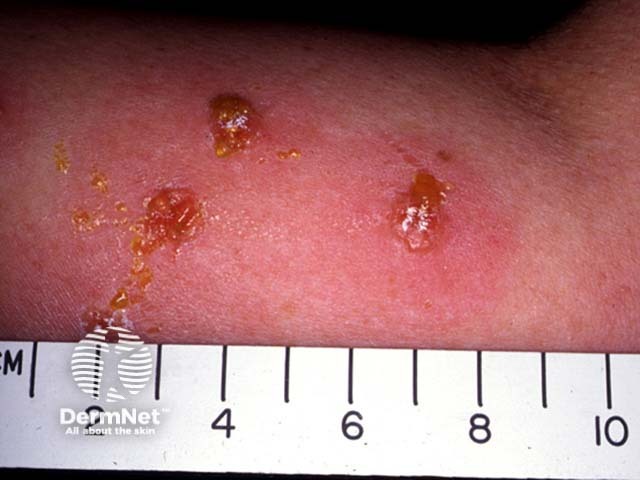
Microsporum canis
Palmoplantar pustulosis
- Hands, feet
- Sterile tender, itchy, pustules
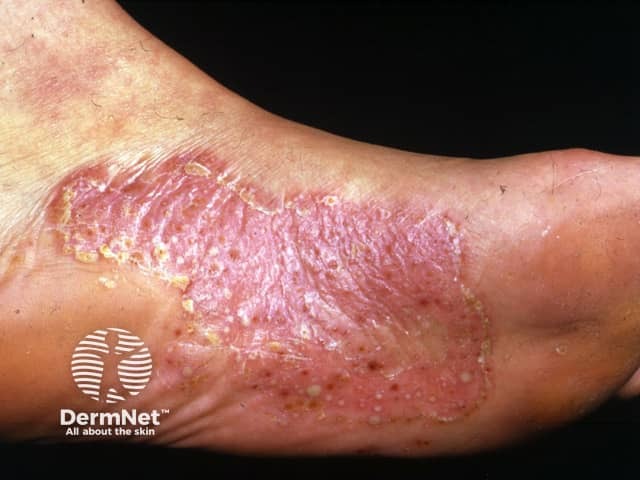
Palmoplantar pustulosis
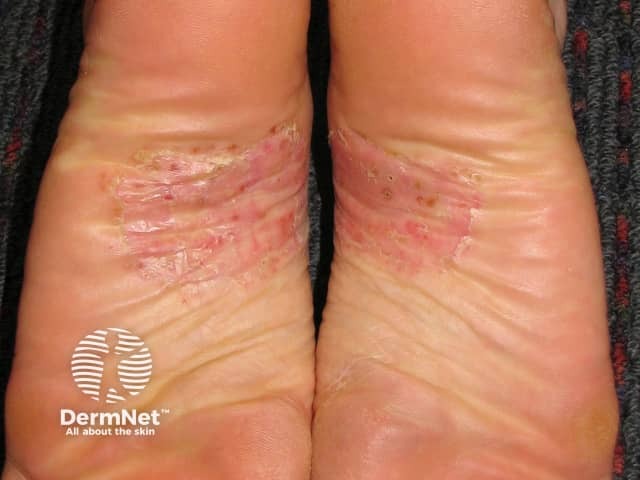
Palmoplantar pustulosis
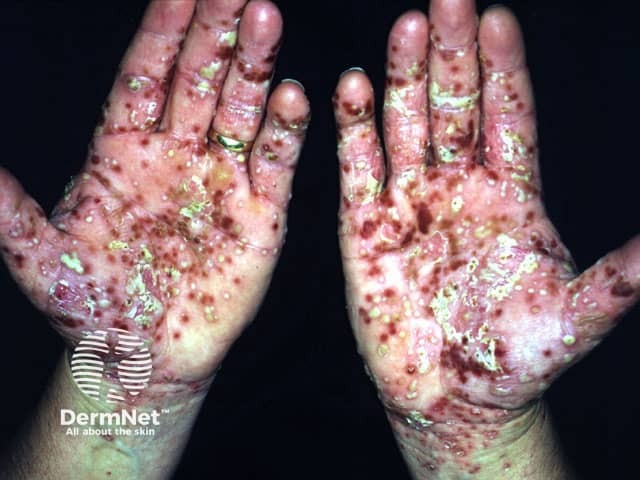
Palmoplantar pustulosis
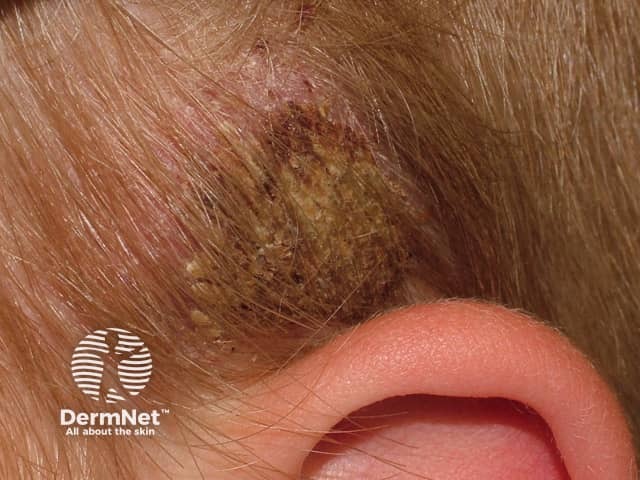
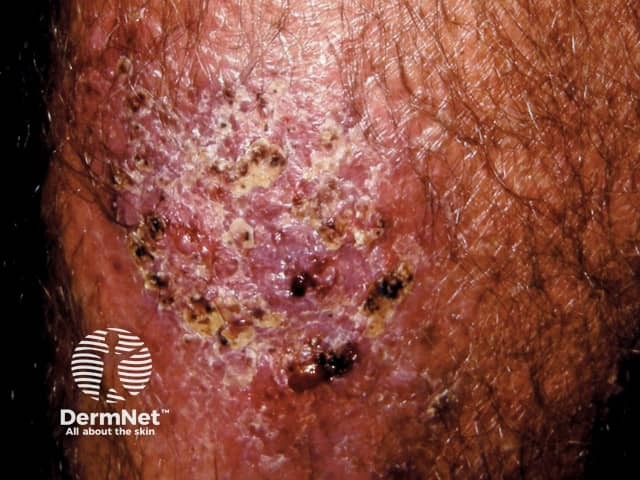
Erosive pustular dermatosis
- Sun damaged scalp
- May develop squamous cell carcinoma
- Lakes of greenish pus
- Culture may reveal Staphylococcus aureus
Many skin conditions present with pustules - see links to more On DermNet in the Related Information Section below.
Bibliography
- Bachelez H. Pustular psoriasis and related pustular skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(3):614-18. doi:10.1111/bjd.16232 PubMed
- Filosa A, Filosa G. Neutrophilic dermatoses: a broad spectrum of disease. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153(2):265-72. doi:10.23736/S0392-0488.18.05841-8 Journal
- Kutlubay Z, Tanakol A, Engýn B, et al. Newborn Skin: Common Skin Problems. Maedica (Bucur). 2017;12(1):42-7. PubMed Central
- Mengesha YM, Bennett ML. Pustular skin disorders: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3(6):389-400. doi:10.2165/00128071-200203060-00003 PubMed
On DermNet
- Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
- Acute localised exanthematous pustulosis
- Blistering skin conditions
- Blisters and pustules in neonates
- Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis
- Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis of infancy
- Gonorrhoea
- Gram-negative folliculitis
- Neutrophilic dermatoses
- Neutrophilic dermatosis of the hands
- Orf
- Neonatal cephalic pustulosis
- Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy
- Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans
- Scalp folliculitis
- Subcorneal pustular dermatosis
- Toxic erythema of the newborn
- Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
Other websites
- Pustules — MedlinePlus
