Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Hon A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, May 2016.
Fever most commonly indicates bacterial or viral infection. If there is no systemic sepsis, localised rashes associated with infection tend to cause fewer systemic symptoms than generalised rashes associated with infection. Mucosal involvement is common. There are some acute auto-inflammatory disorders than mimic infection due to neutrophil activation, the neutrophilic dermatoses.
Consider performing the following tests:
Treatment depends on the cause. Consider referral to the emergency department if you are suspicious of a serious infection or the patient is very unwell.
Consider:
Painful red, hot skin
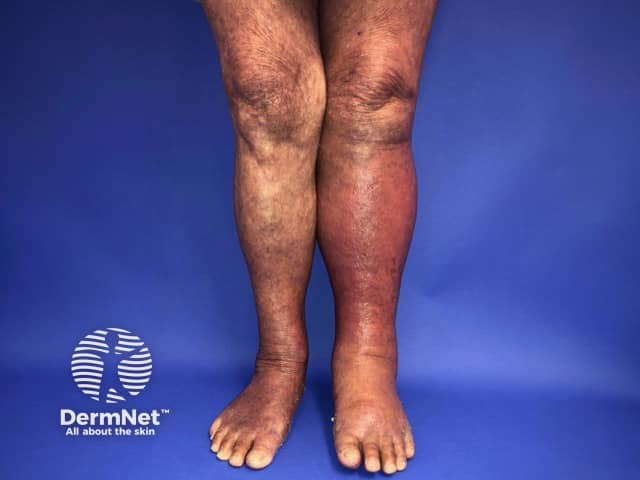
Cellulitis
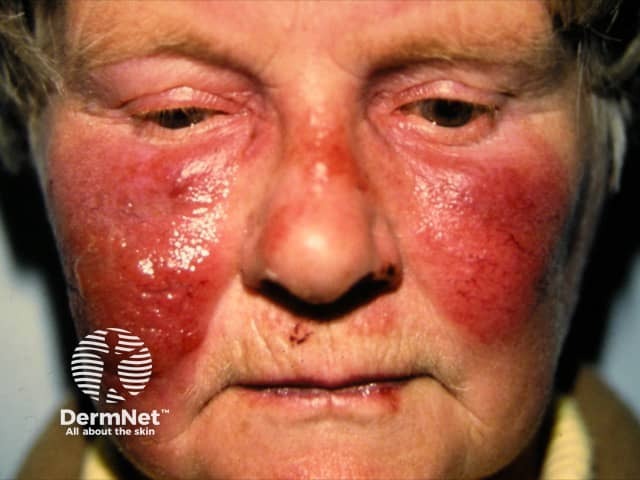
Erysipelas
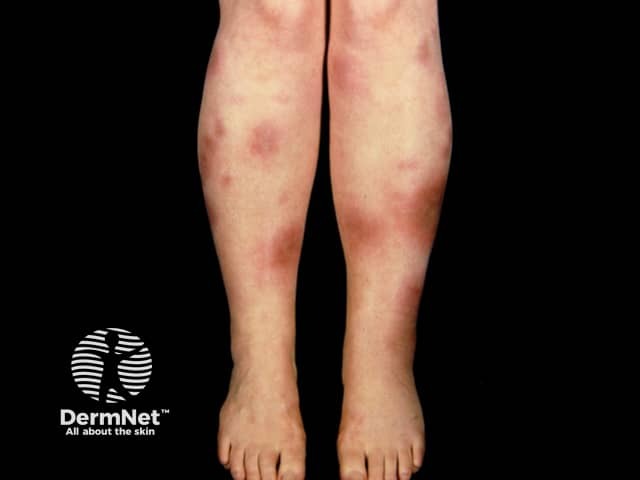
Erythema nodosum
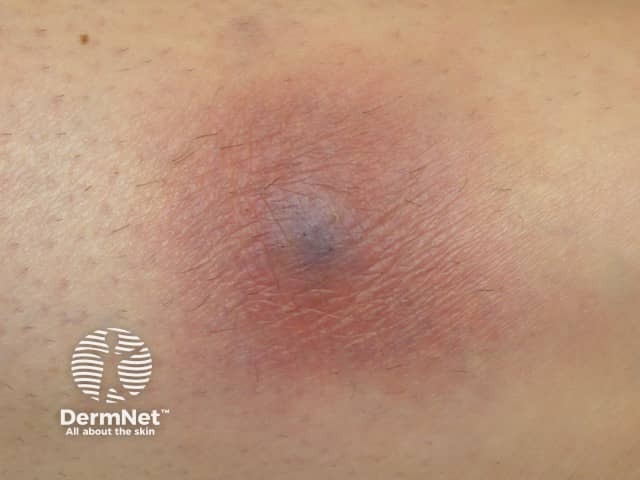
Panniculitis
Prominent blisters/erosions
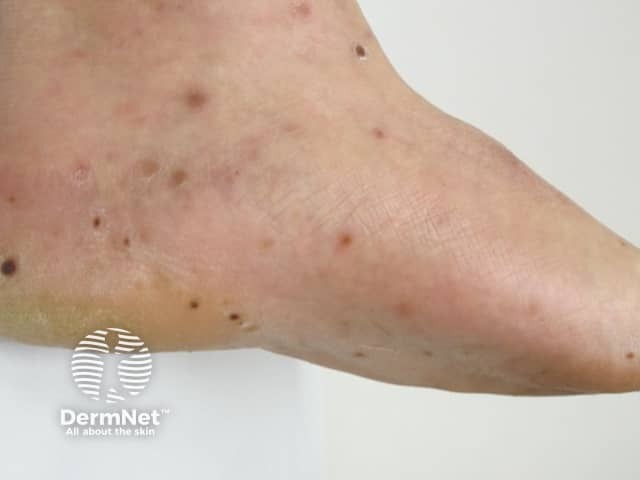
HFM in an adult
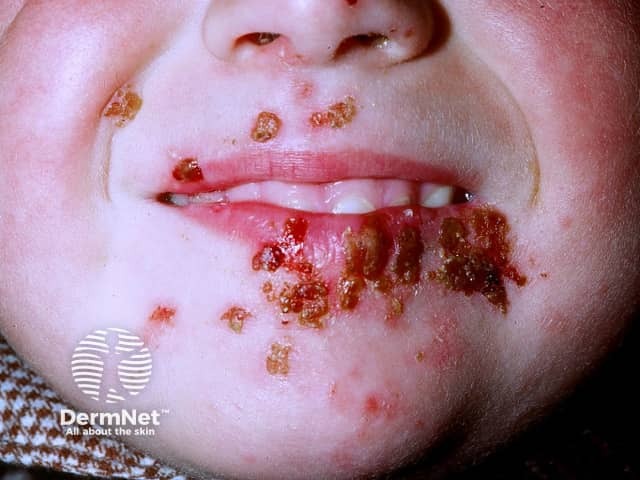
Herpes simplex
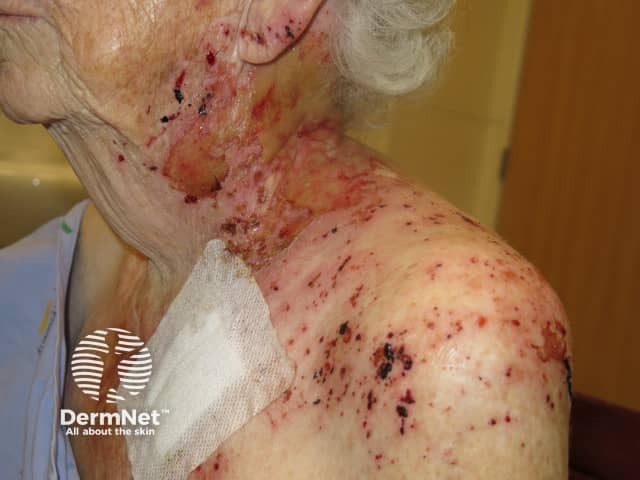
Herpes zoster
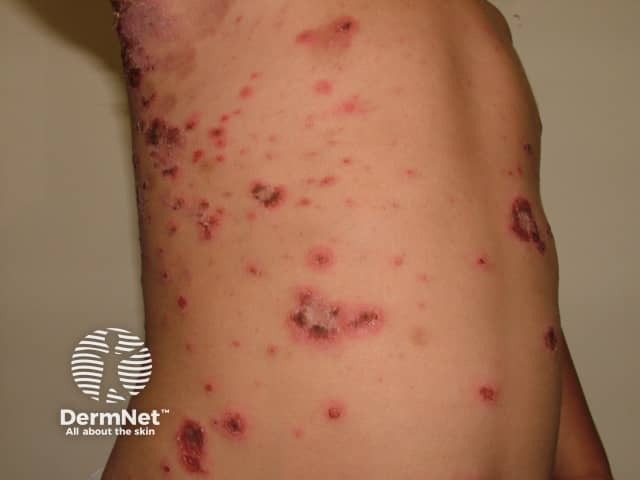
Impetigo
Pustules
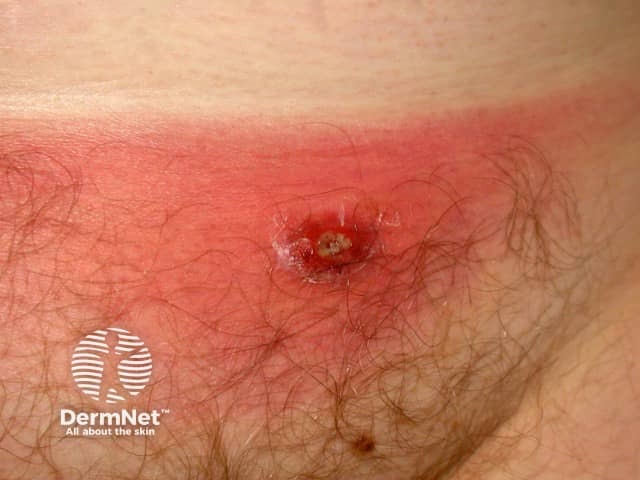
Folliculitis/furunculosis
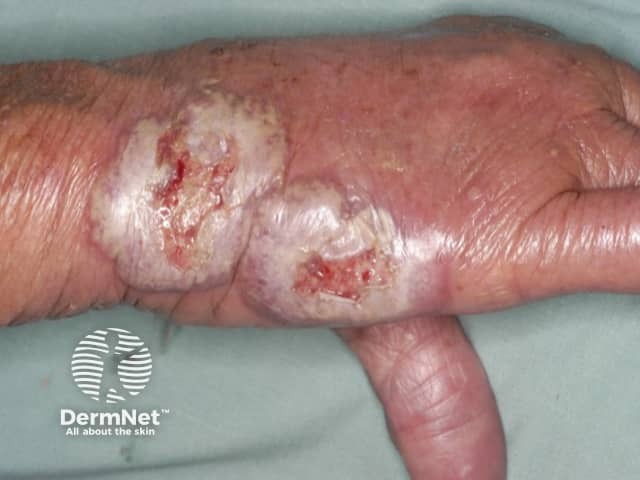
Neutrophilic dermatosis of dorsal hands
Purple/black areas
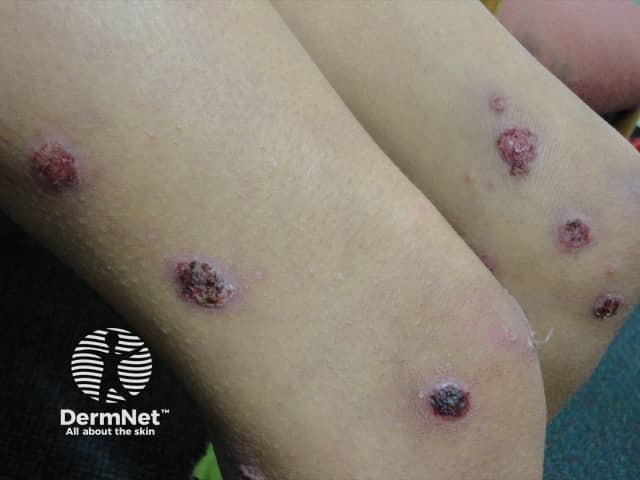
Ecthyma
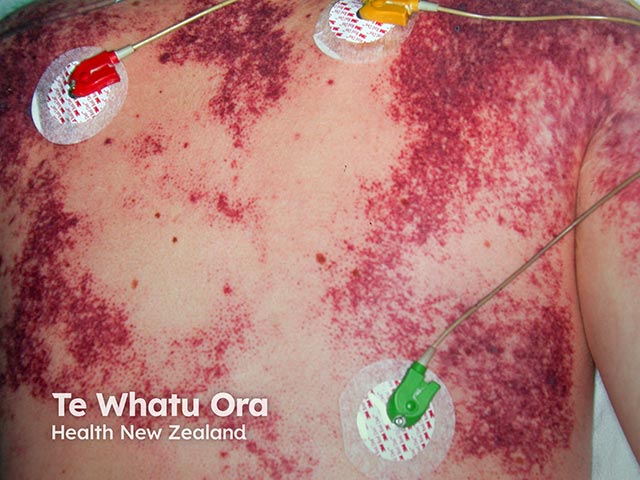
Purpura fulminans
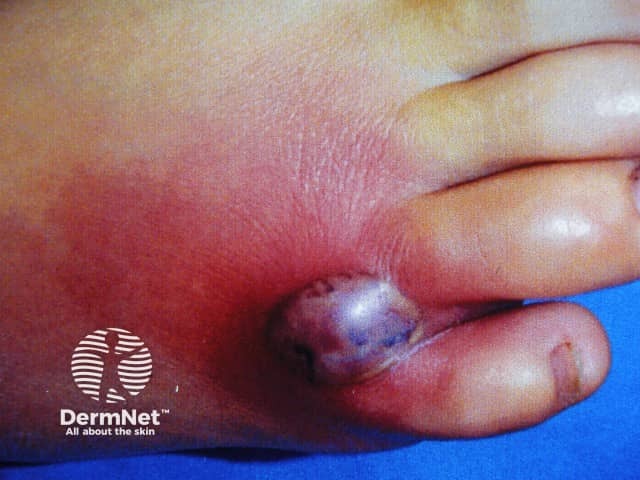
Necrotising spider bite
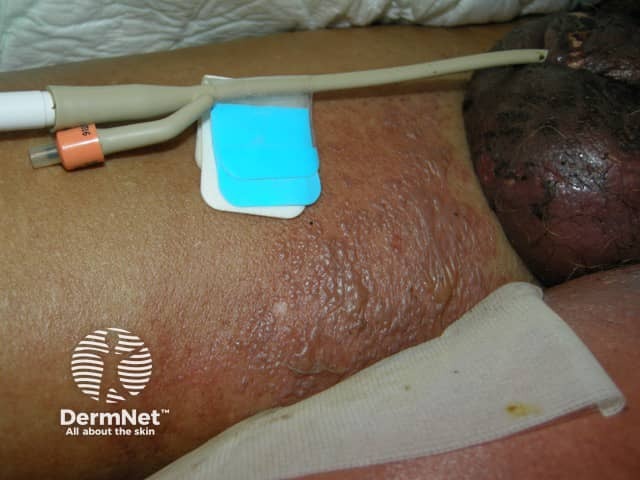
Fournier gangrene
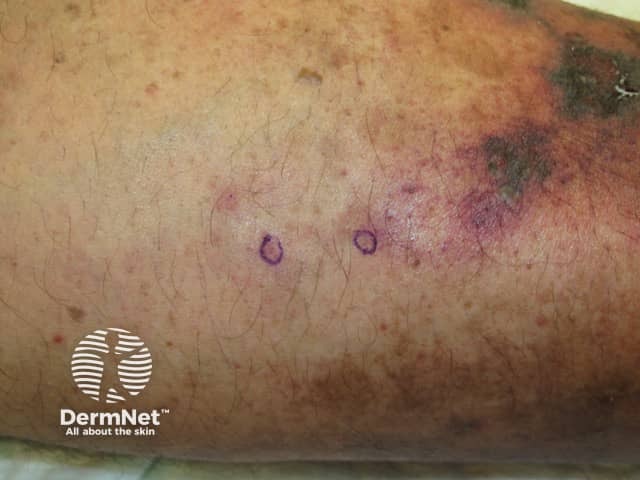
Cholesterol emboli
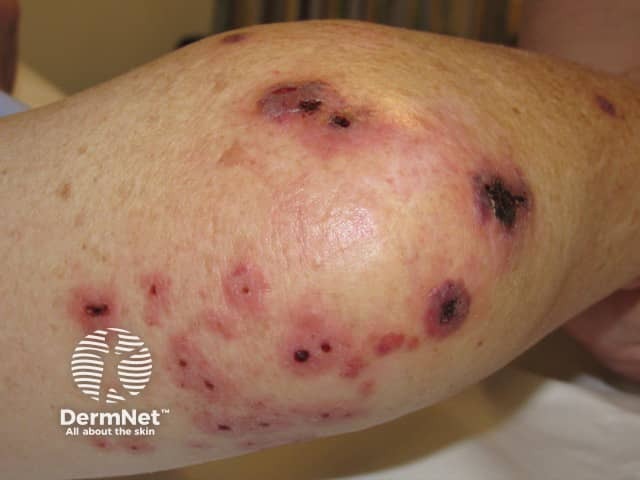
Septic emboli
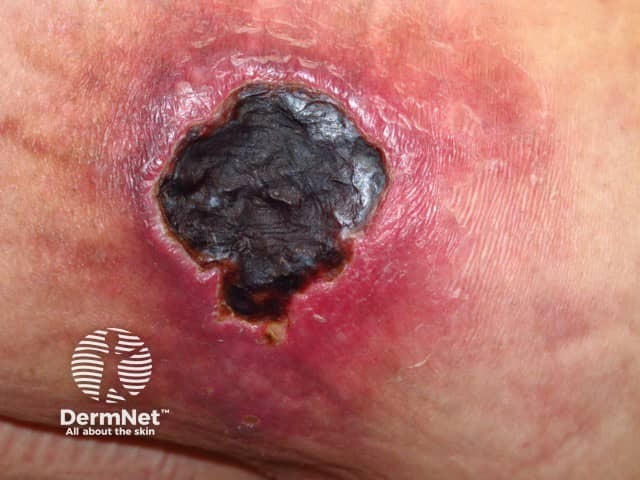
Calciphylaxis
Redness
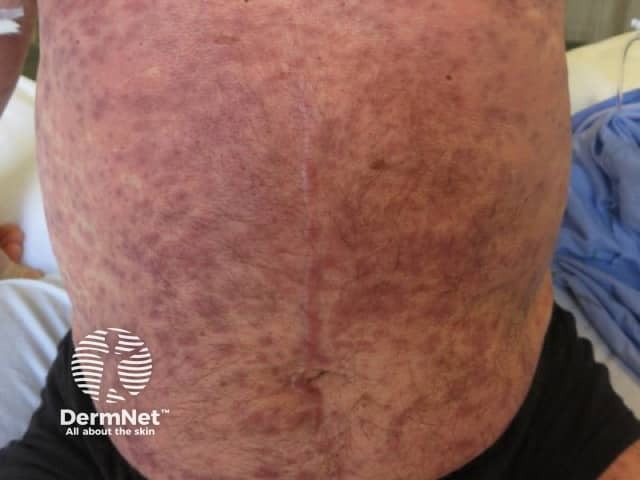
Drug hypersensitivity syndrome
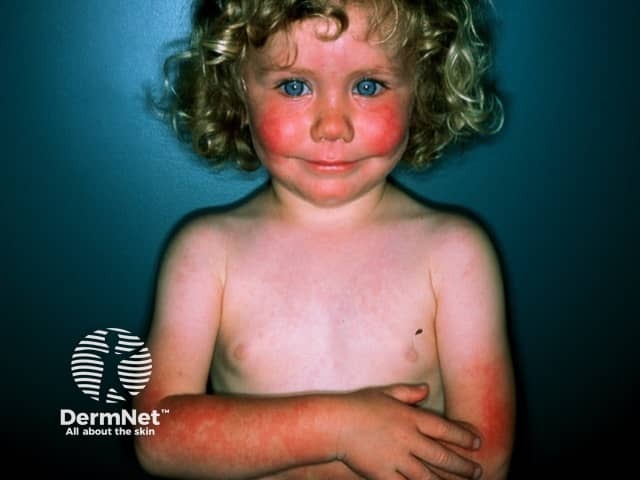
Erythema infectiosum / fifth disease
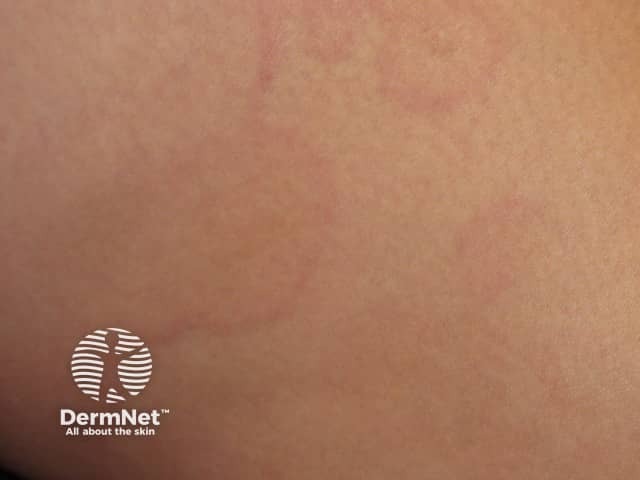
Erythema marginatum
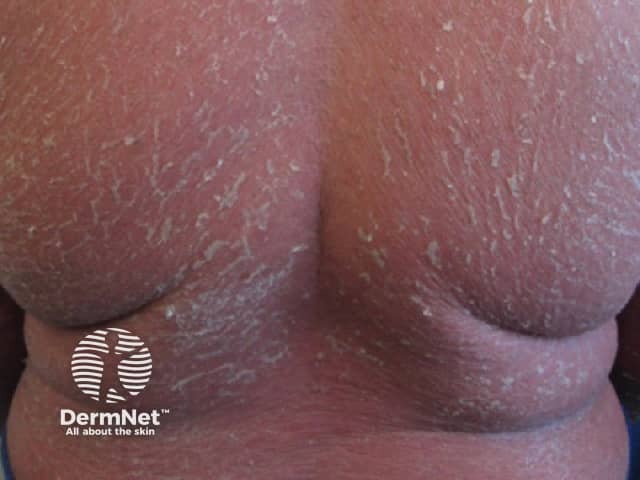
Erythroderma
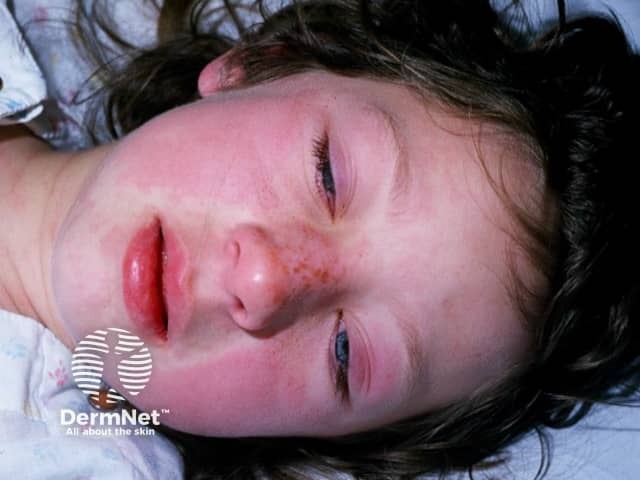
Kawasaki disease
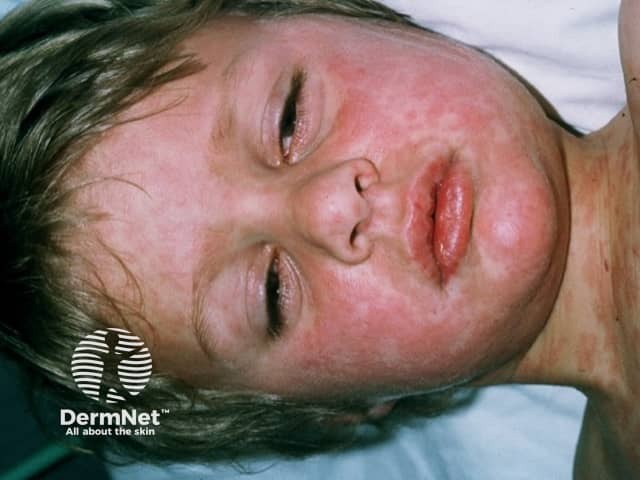
Measles
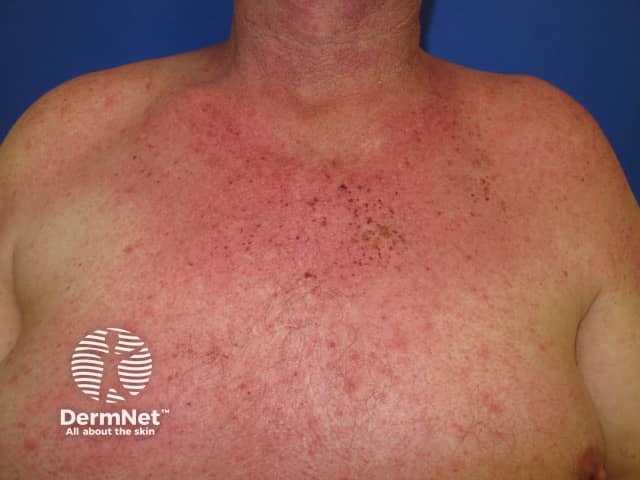
Nonspecific exanthem
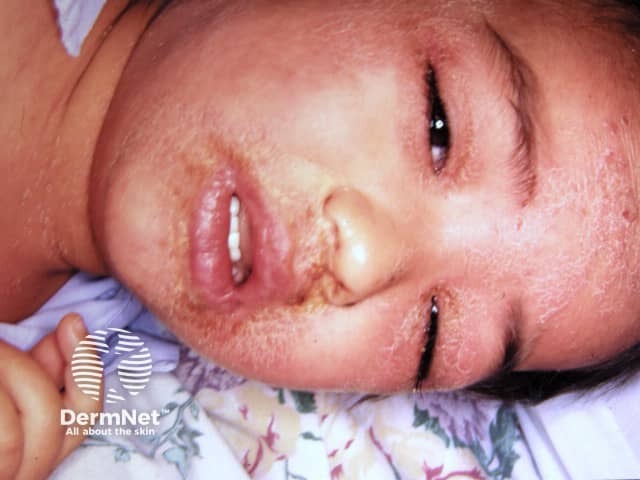
Scarlet fever
Blisters/erosions
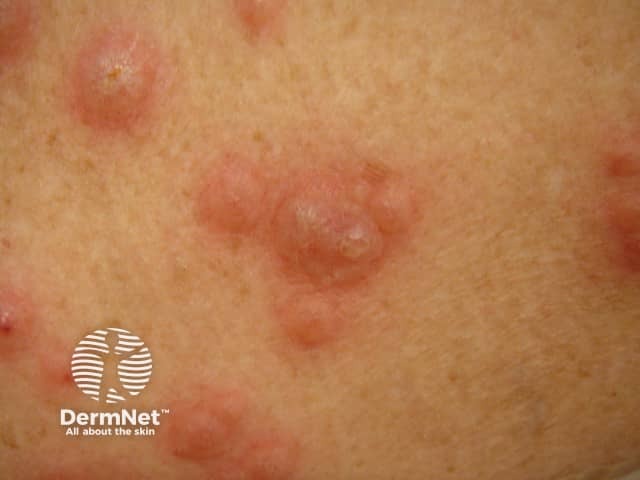
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
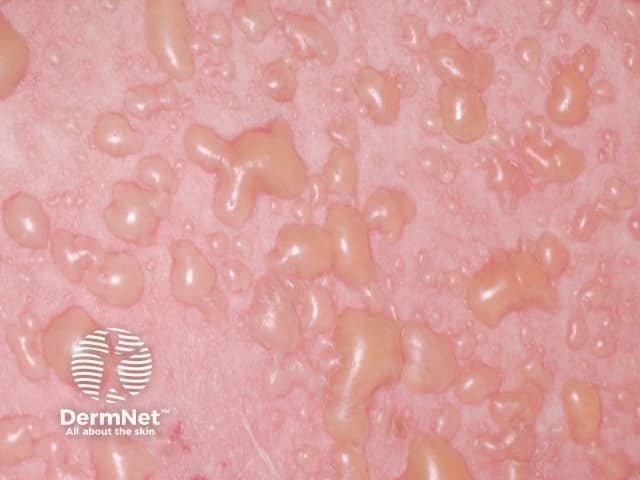
Bullous drug eruption
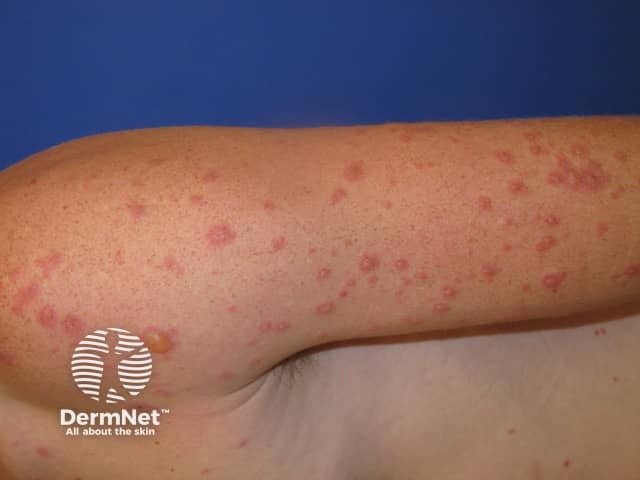
Erythema multiforme
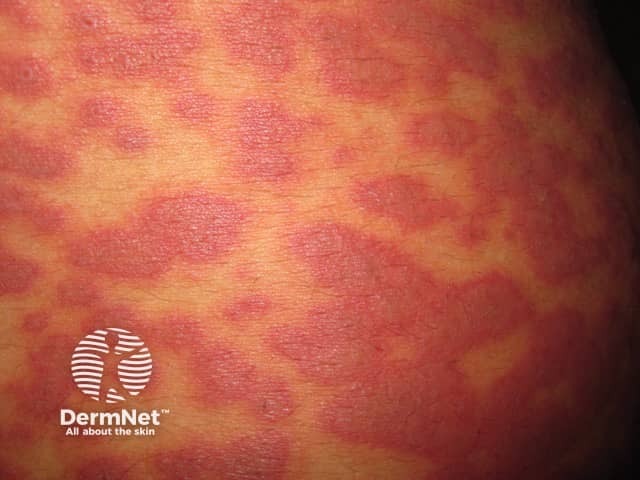
Mycoplasma
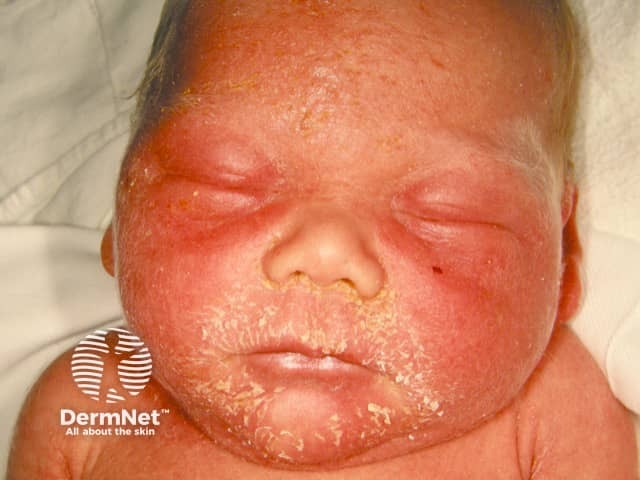
Staphylococcal scalded skin
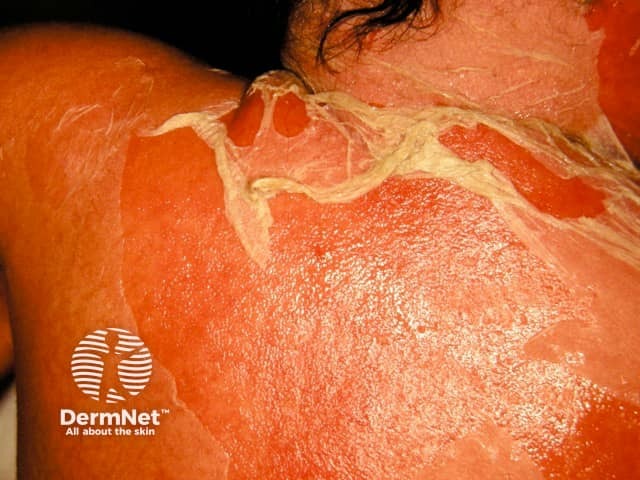
Stevens-Johnson / toxic epidermal necrolysis
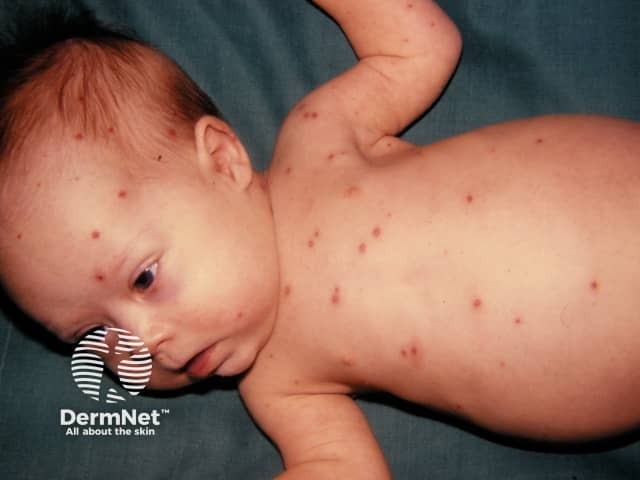
Varicella
Pustules/crusts
May involve mucosal surfaces
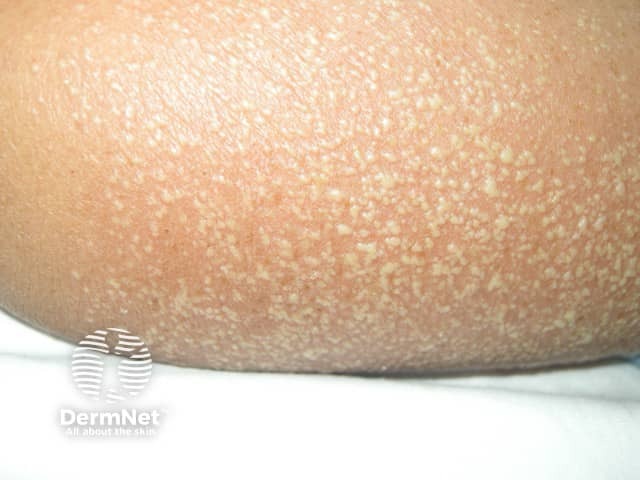
Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis
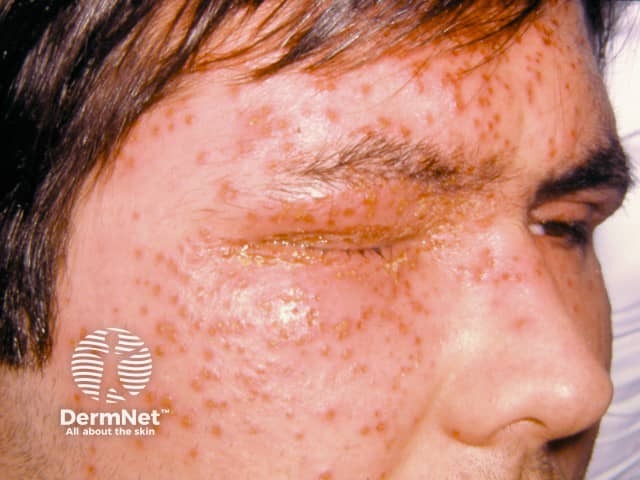
Eczema herpeticum
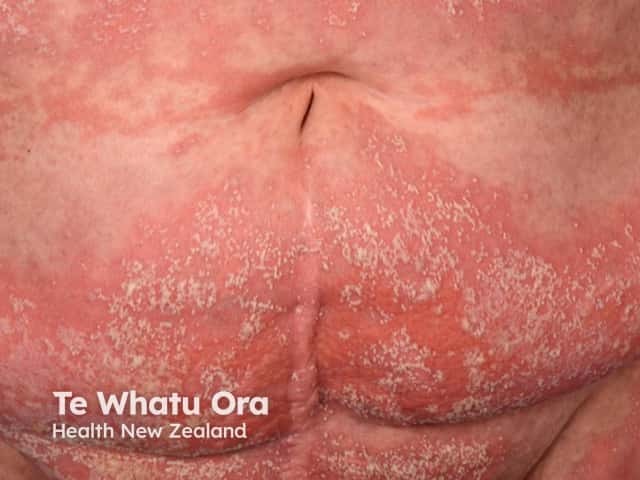
Generalised pustular psoriasis
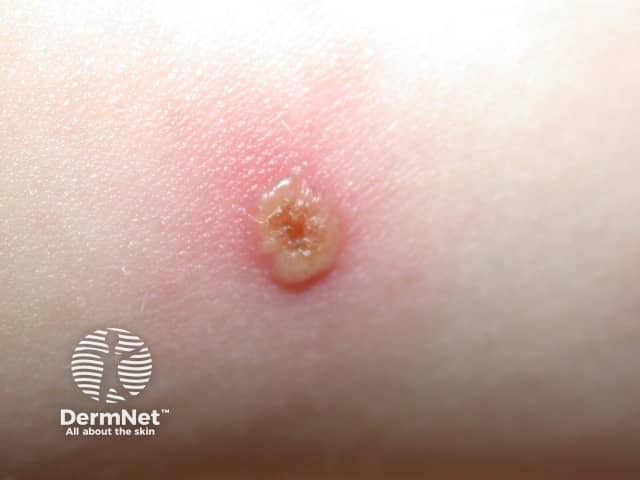
Varicella
Widespread purple/black areas
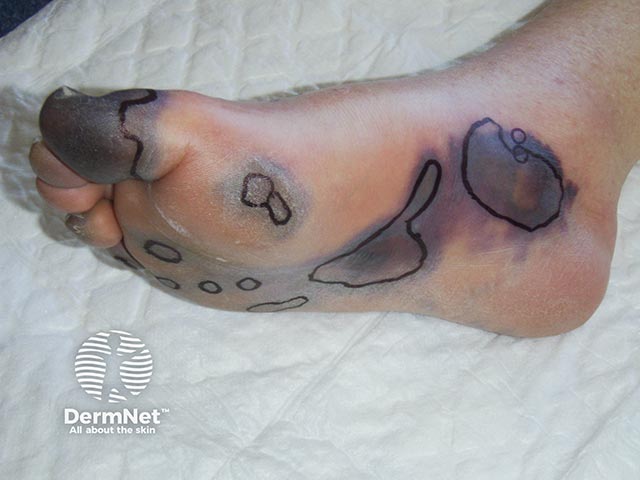
Purpura fulminans / disseminated intravascular coagulation
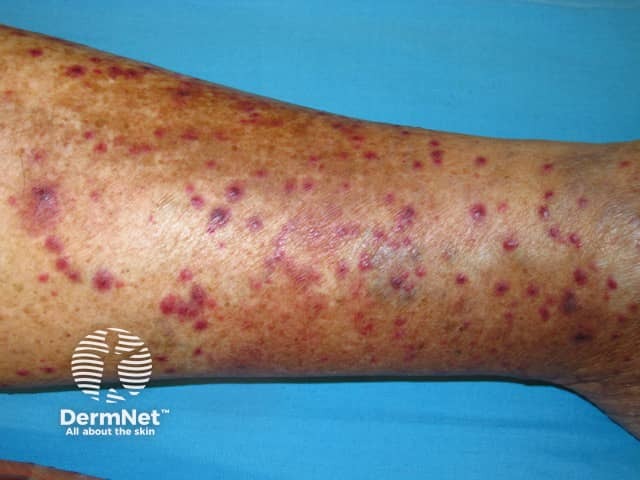
Vasculitis